Preliminary statics
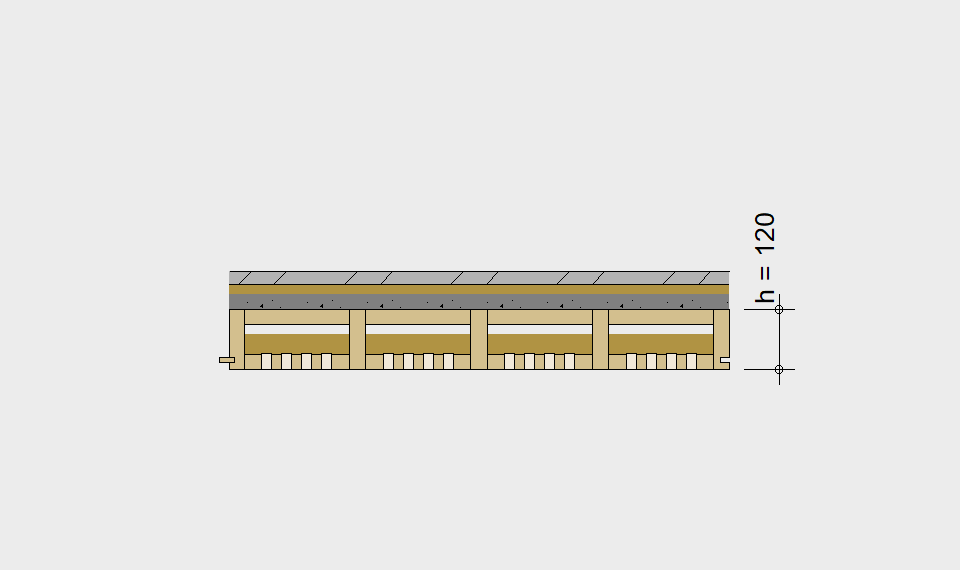
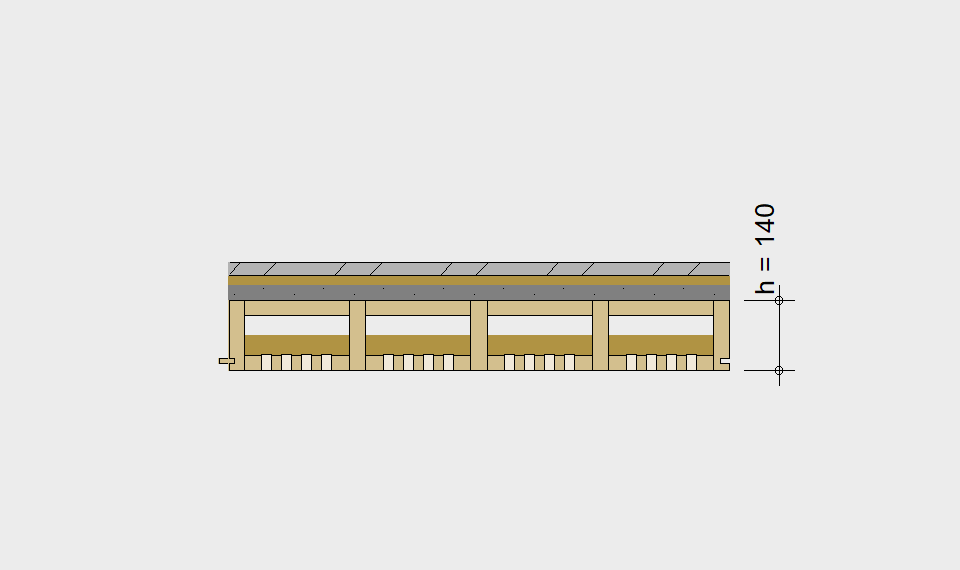
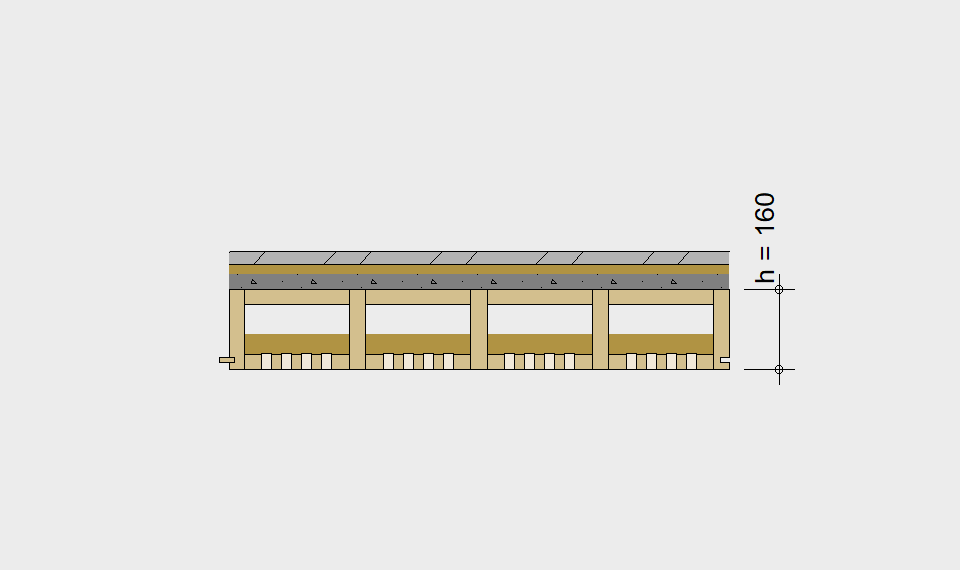
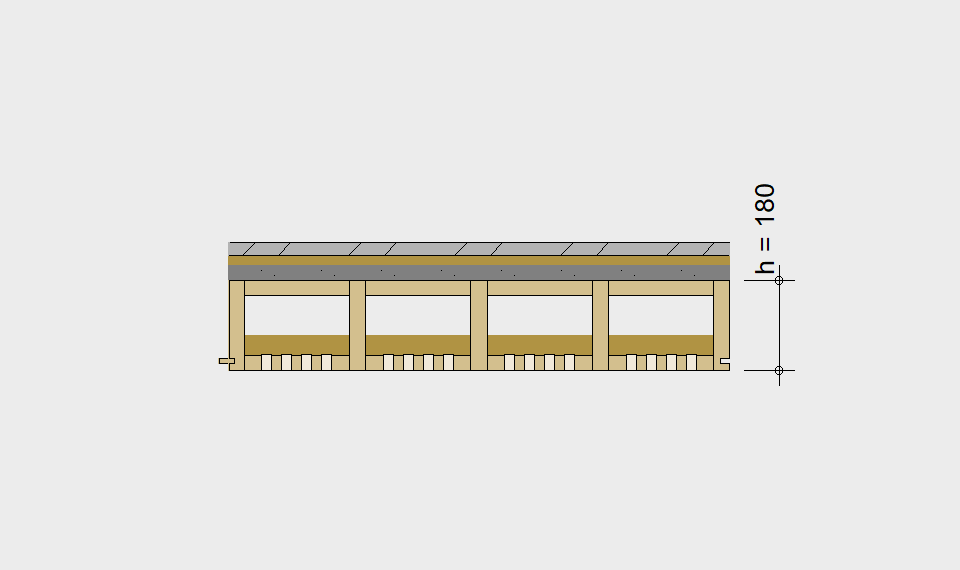
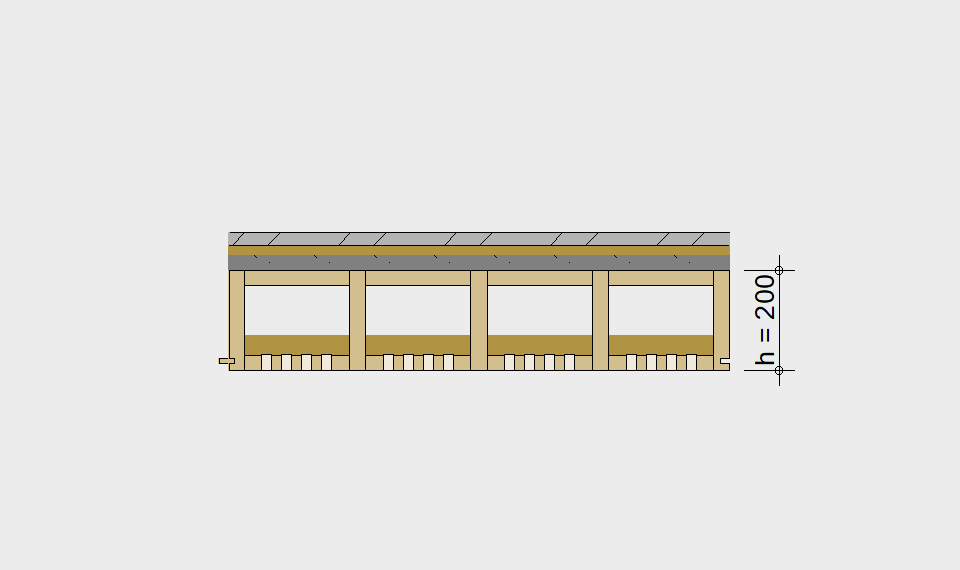
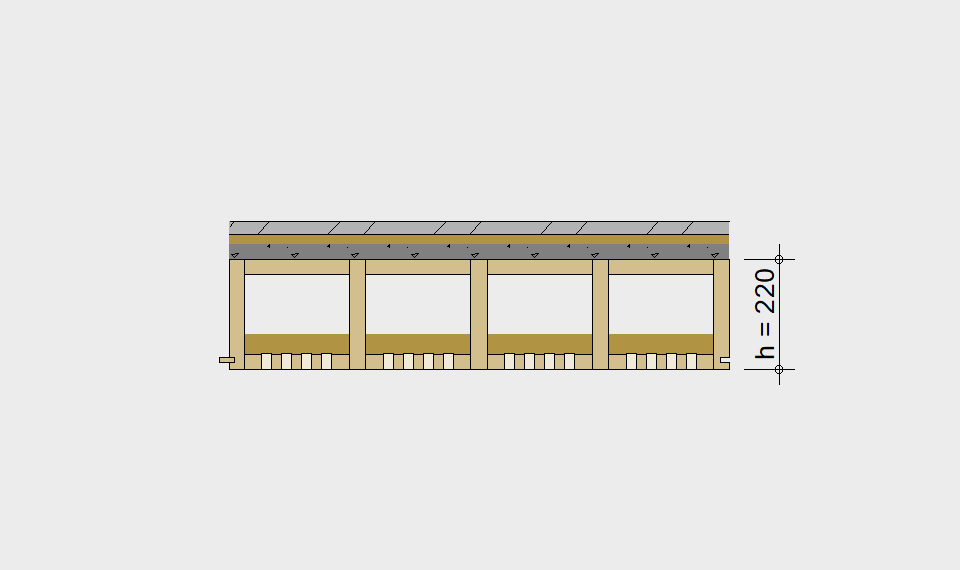
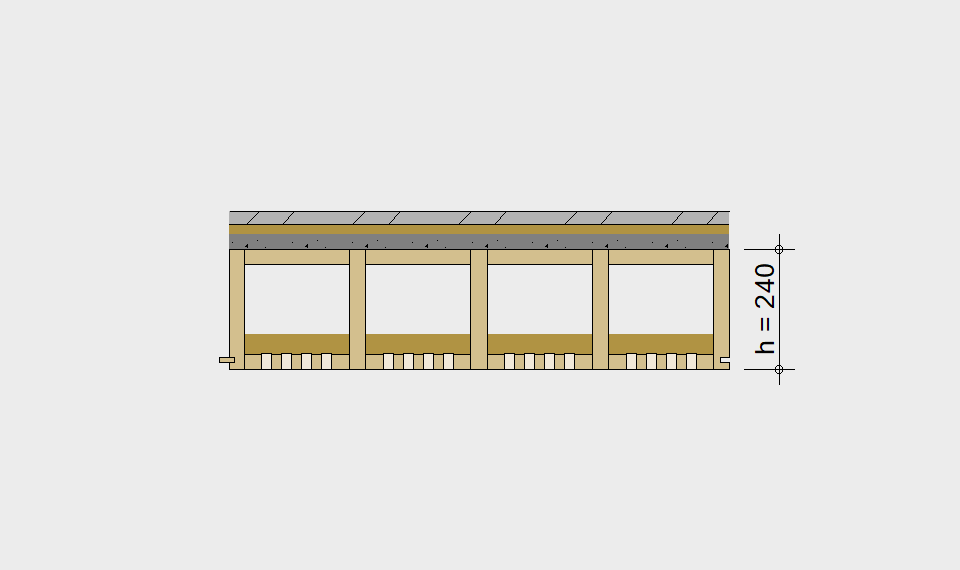
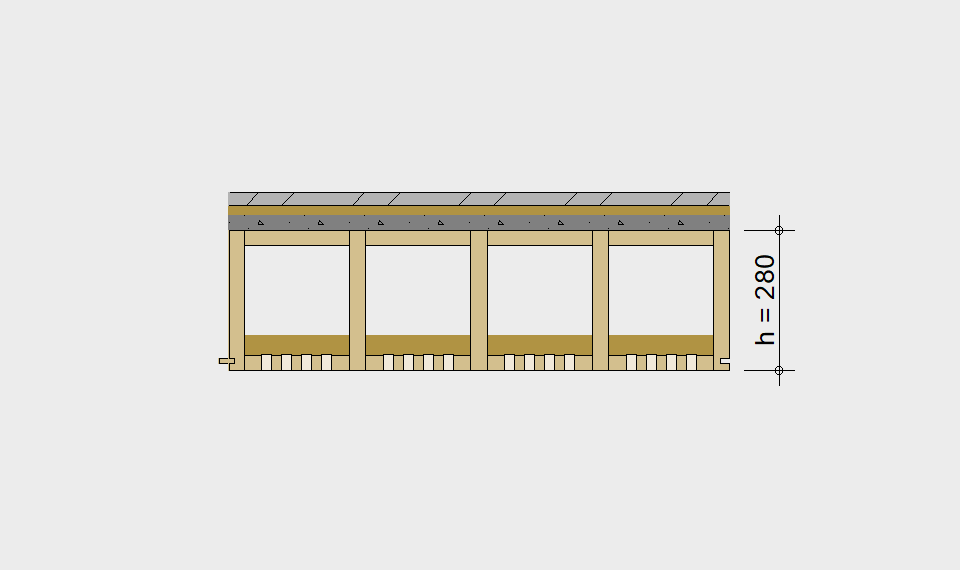
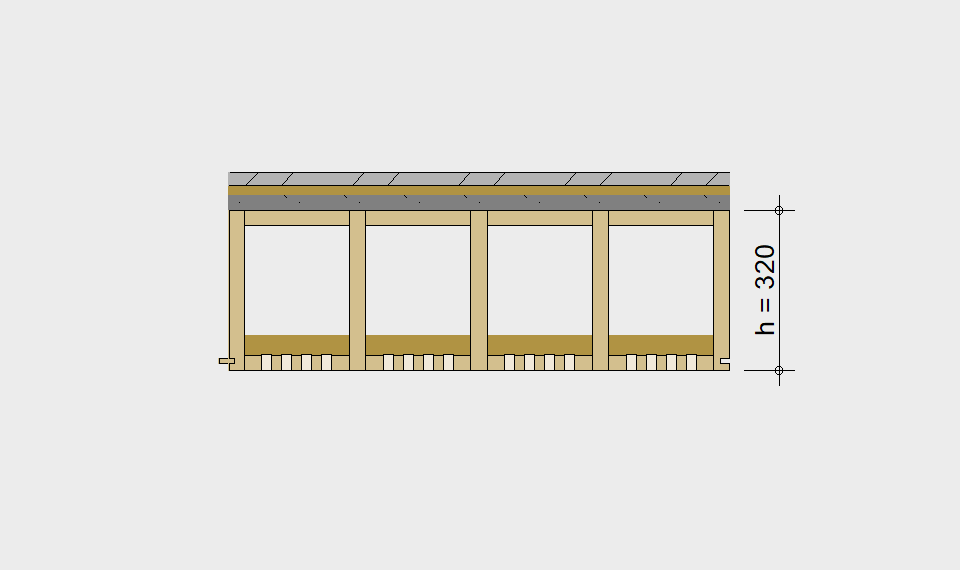
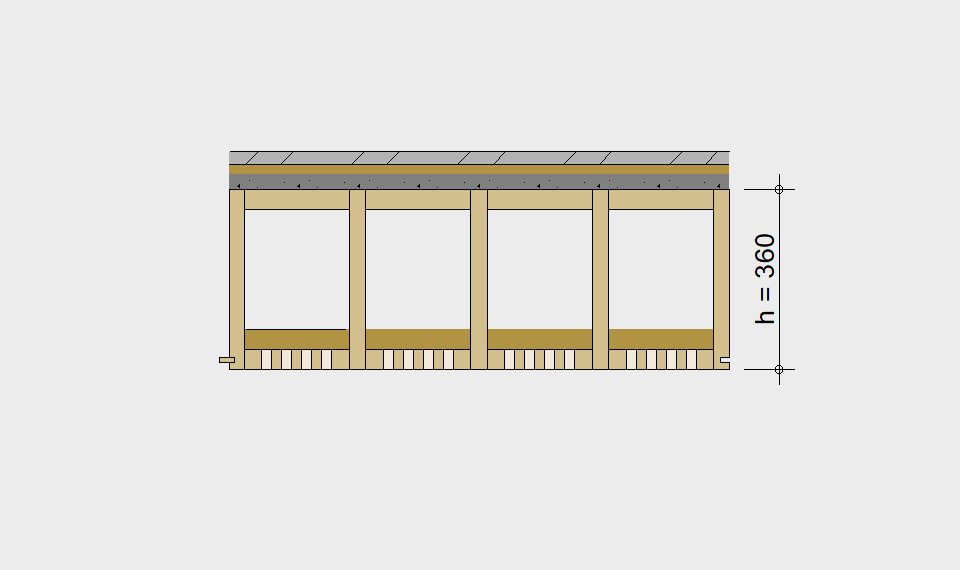
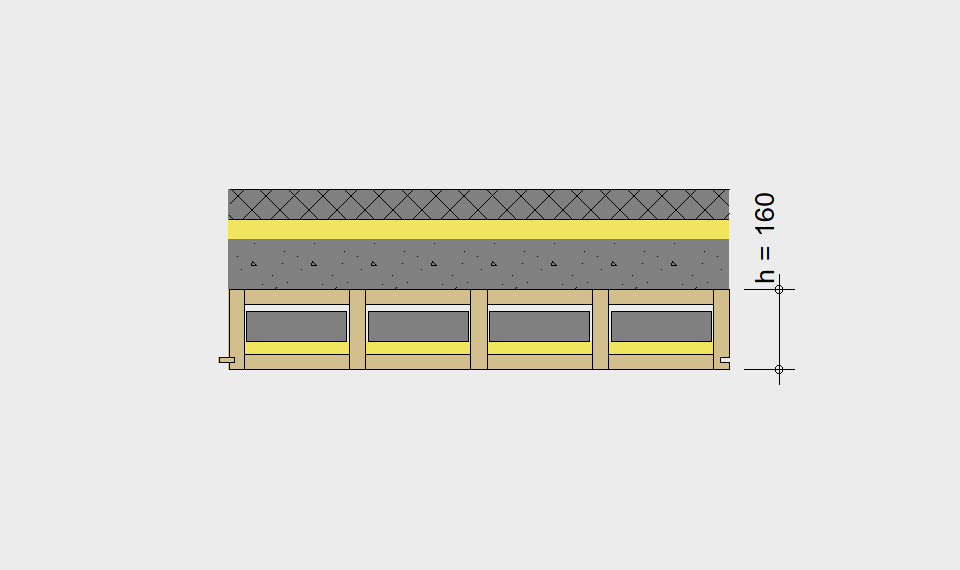
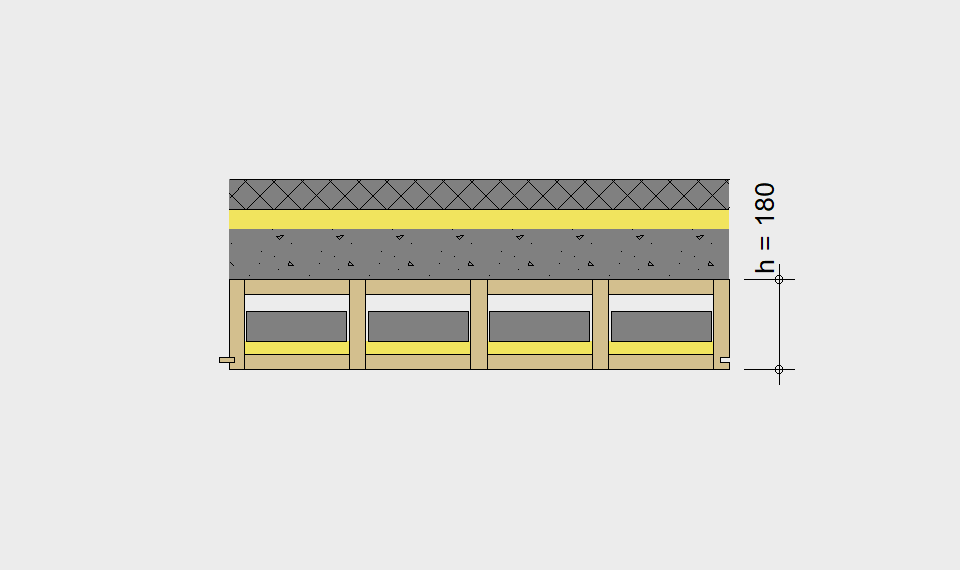
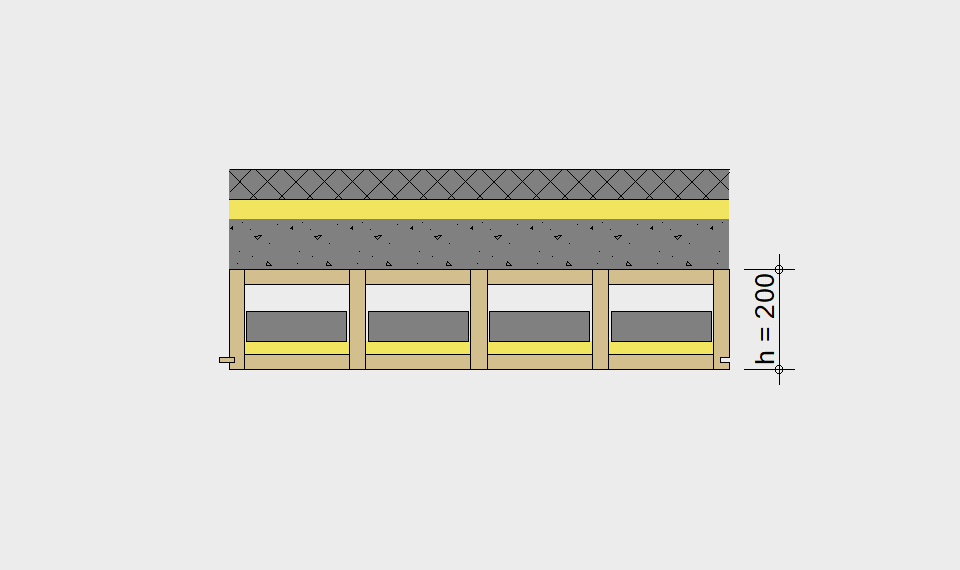
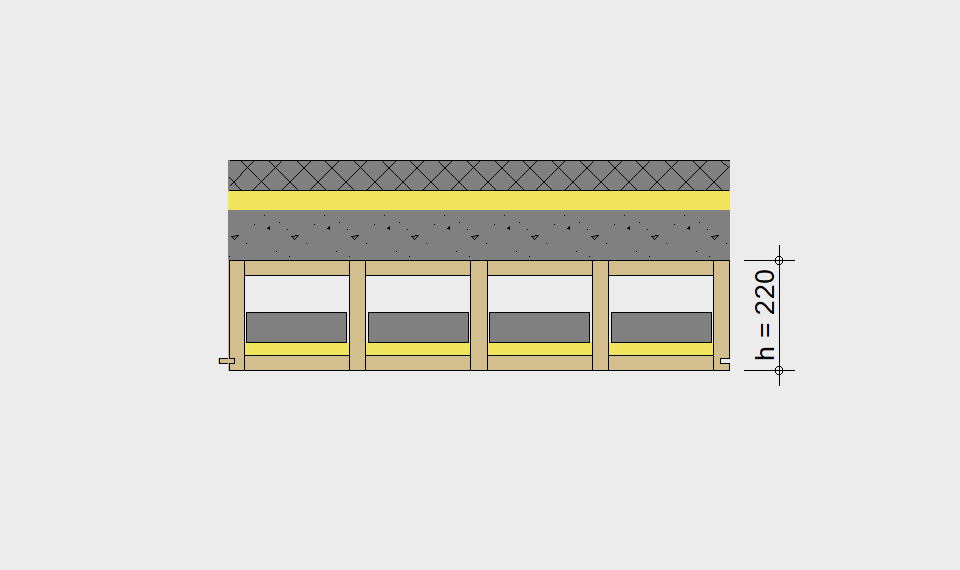
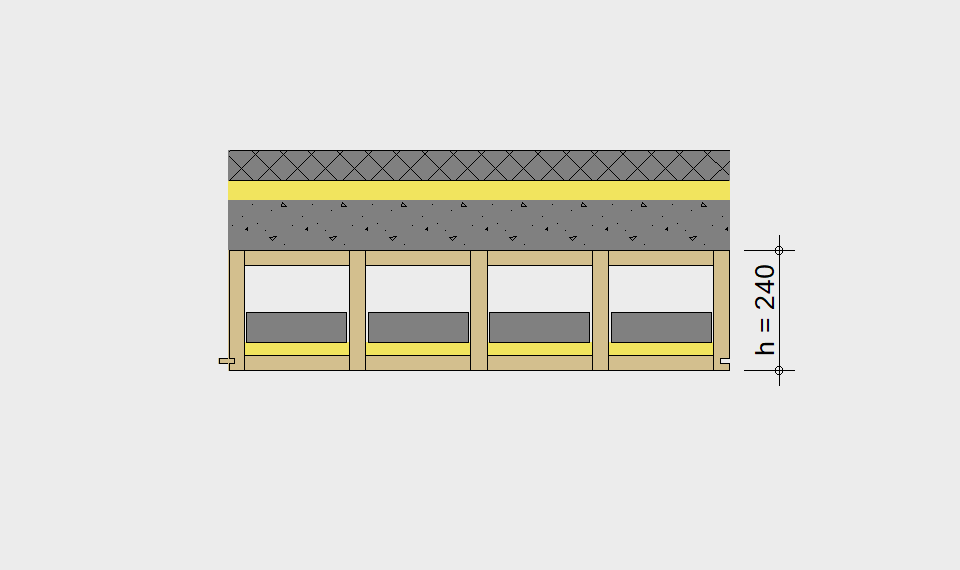
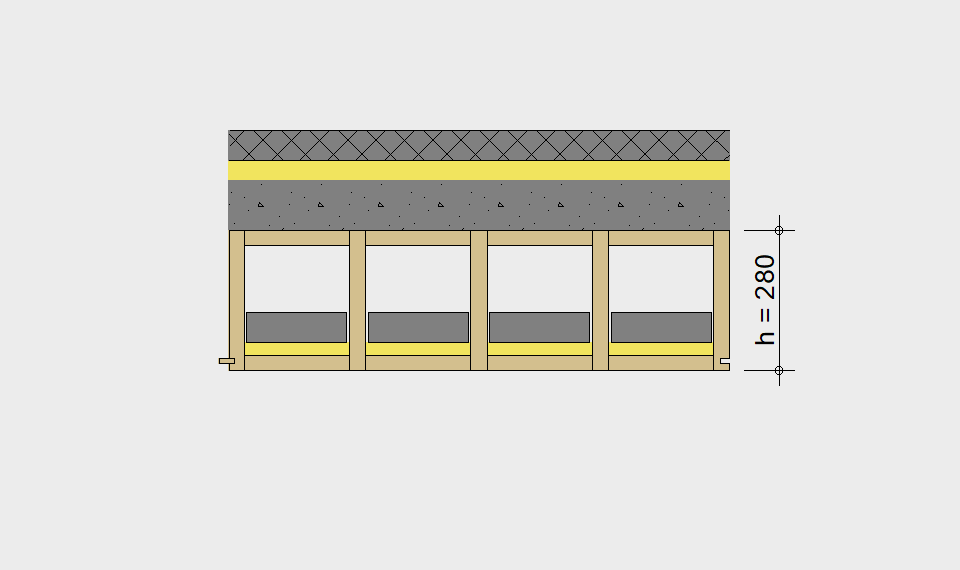
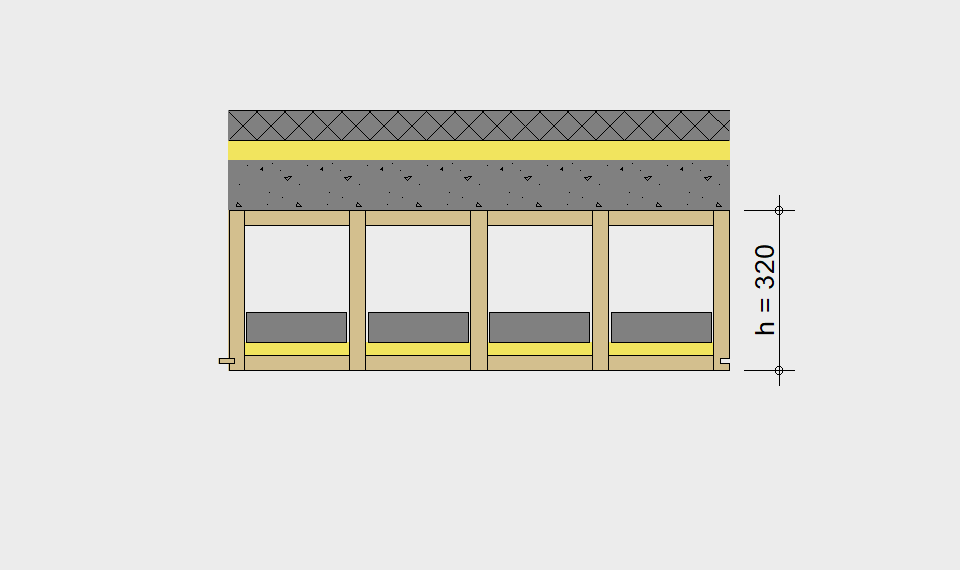
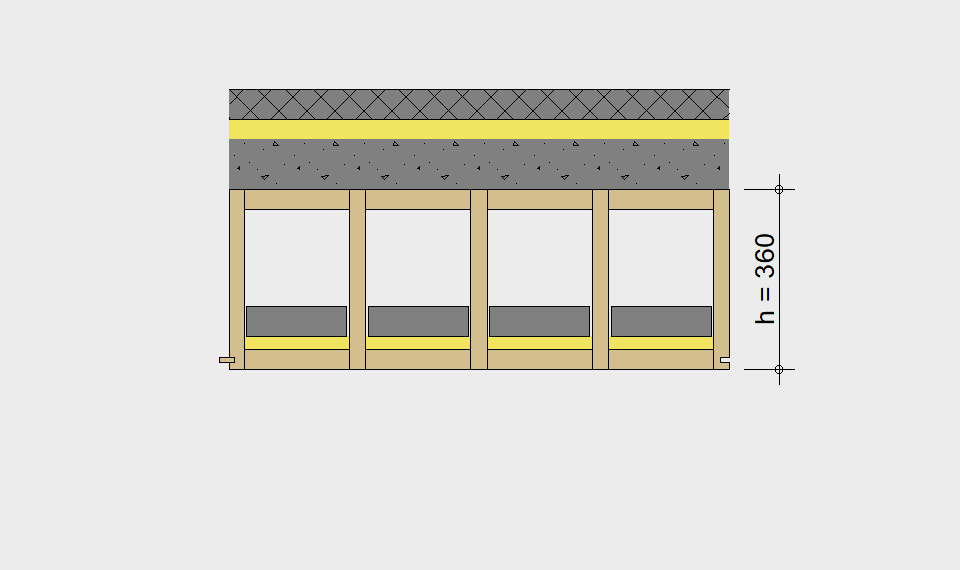
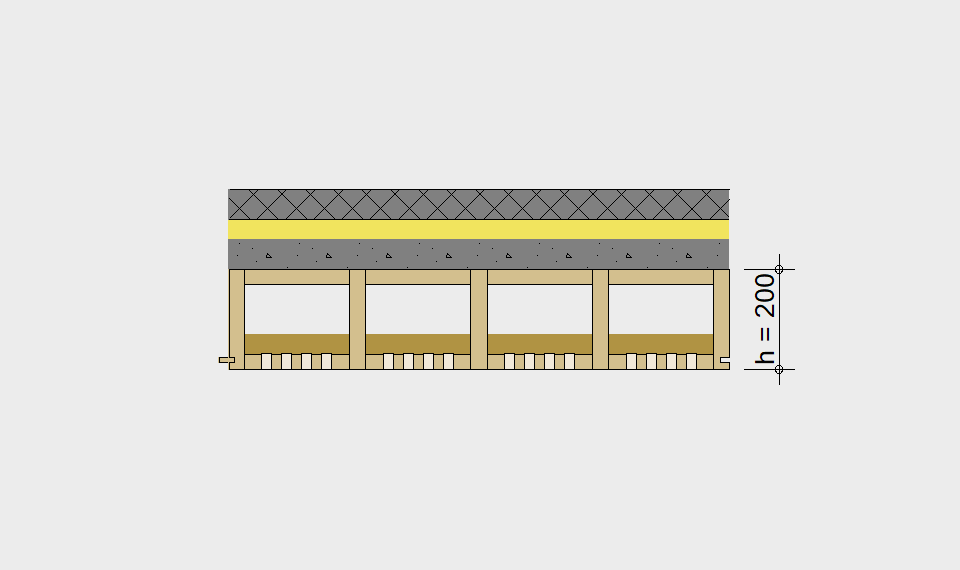
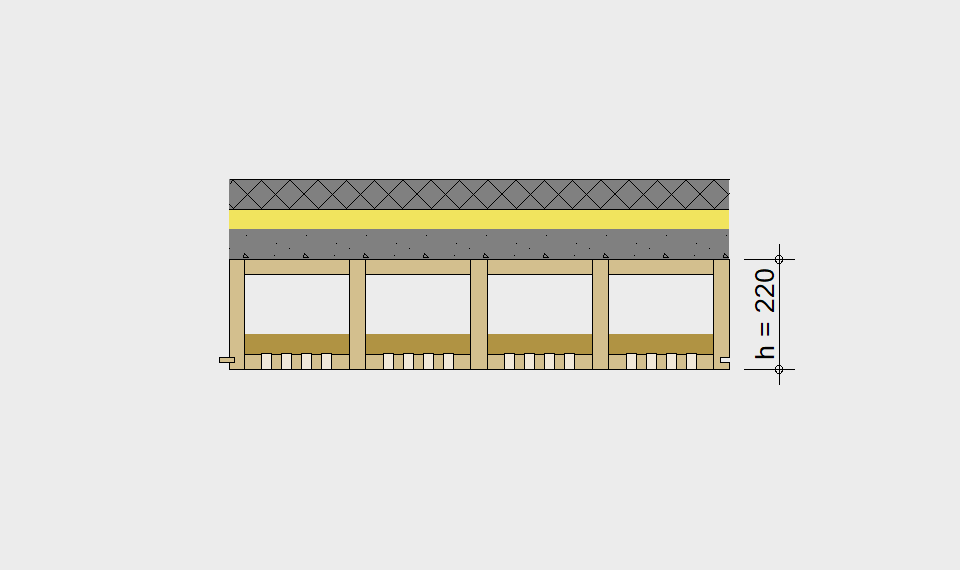
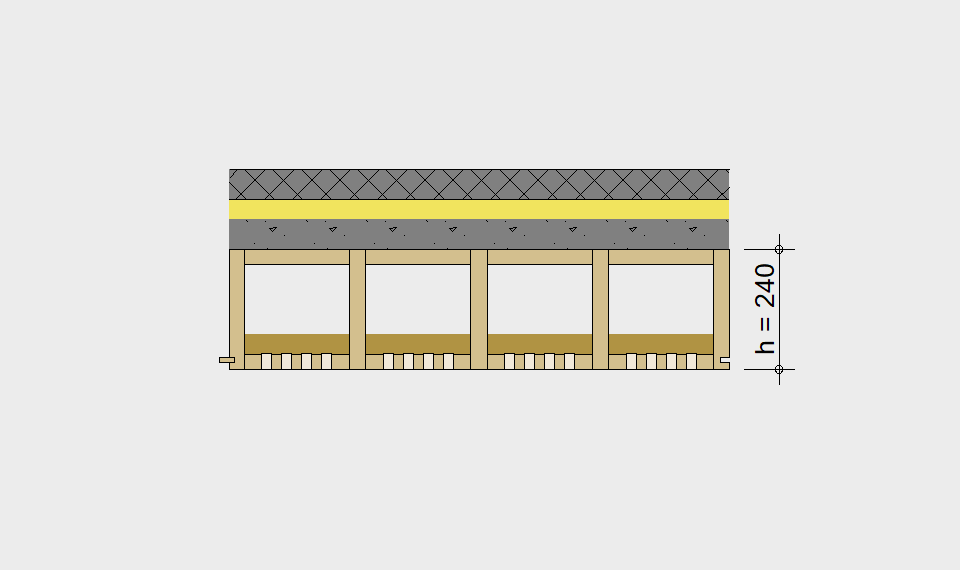
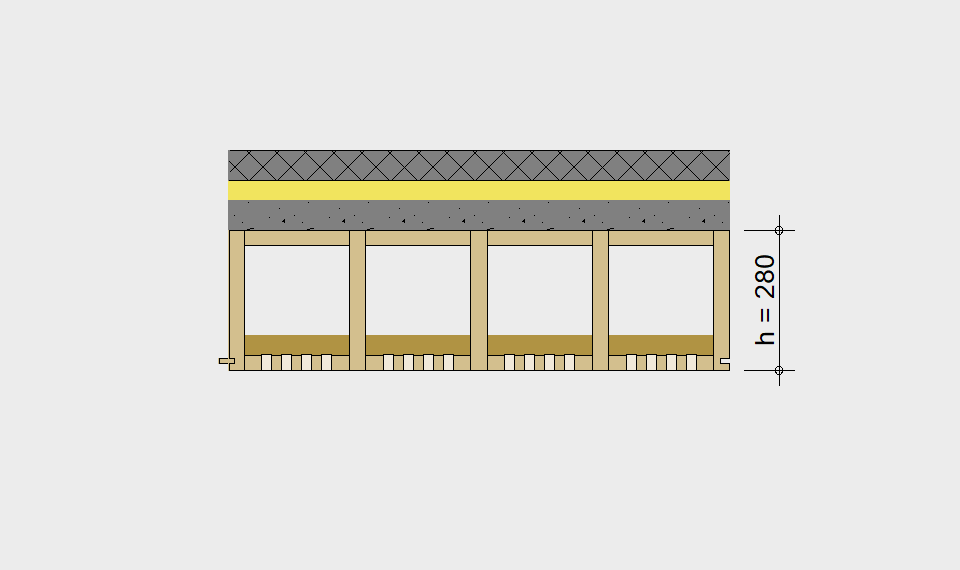
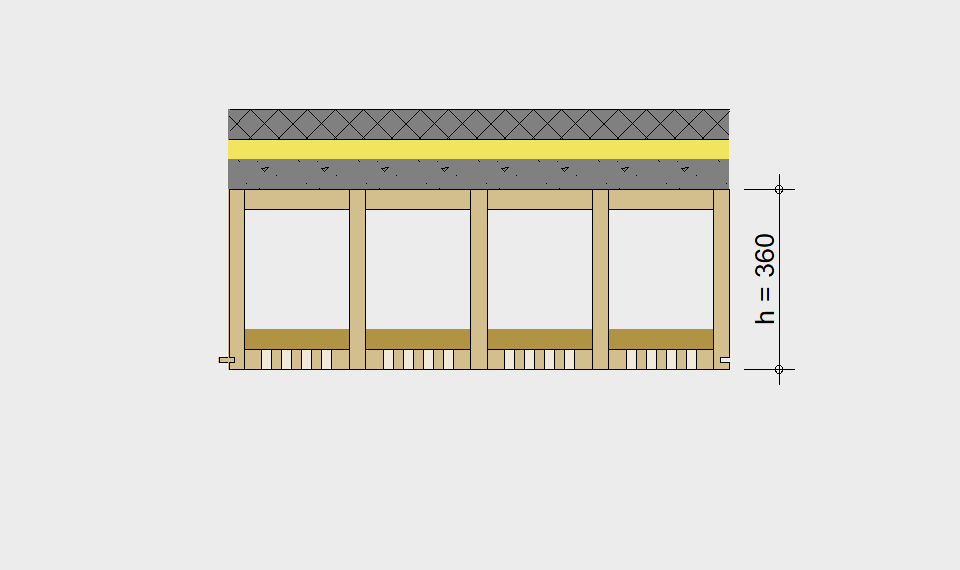
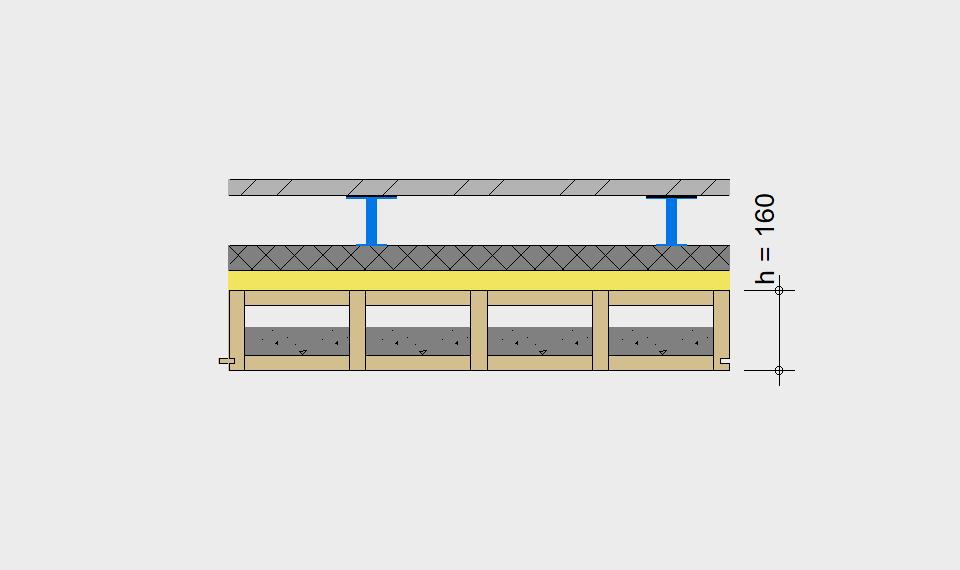
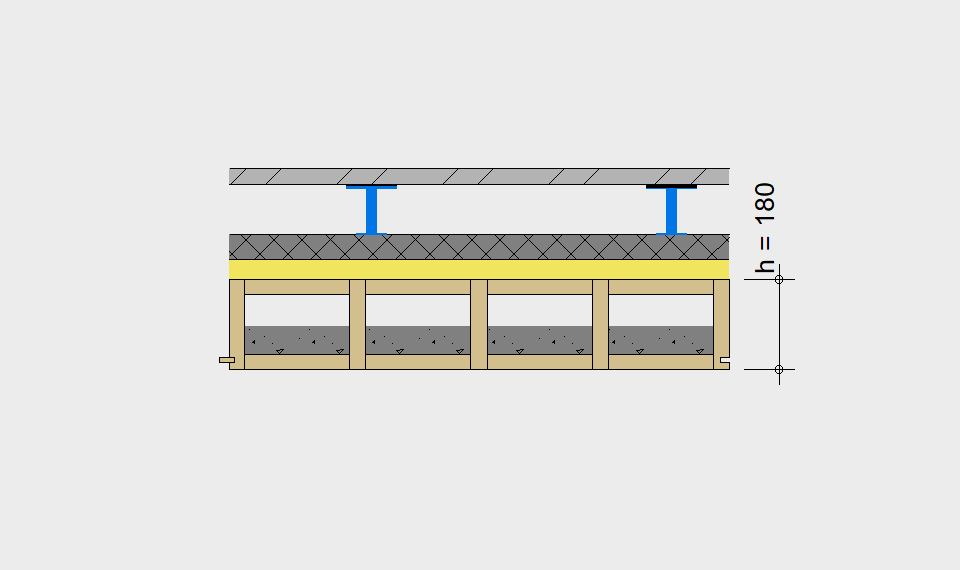
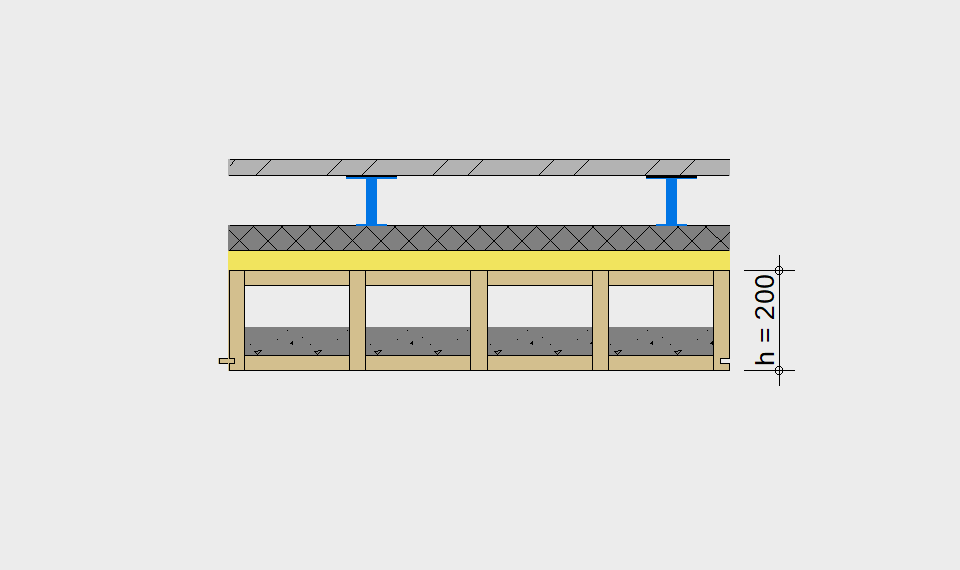
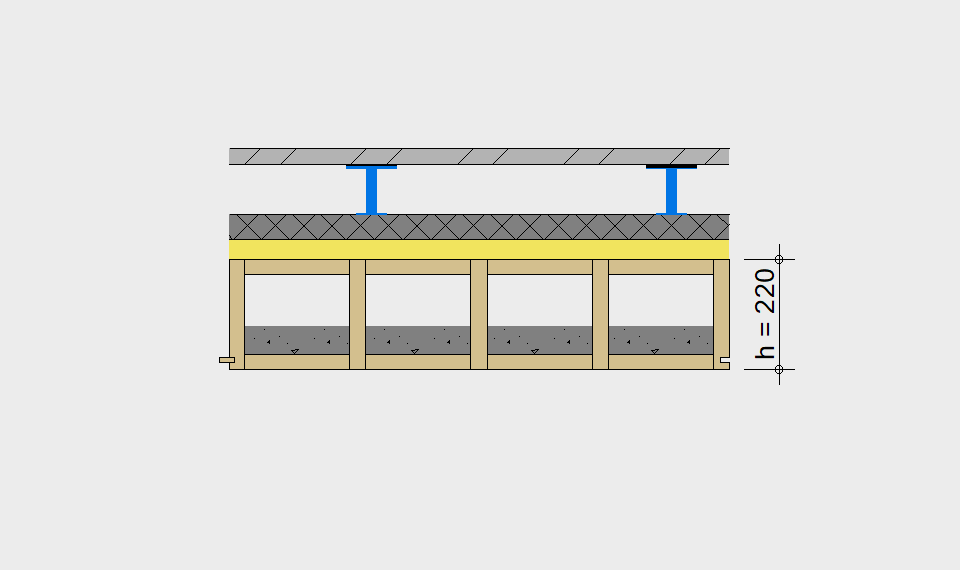
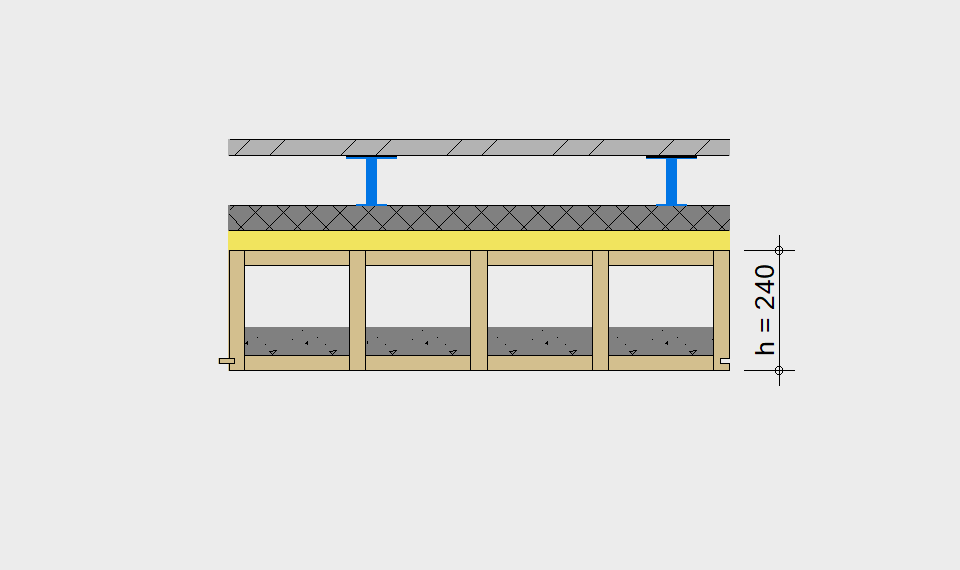
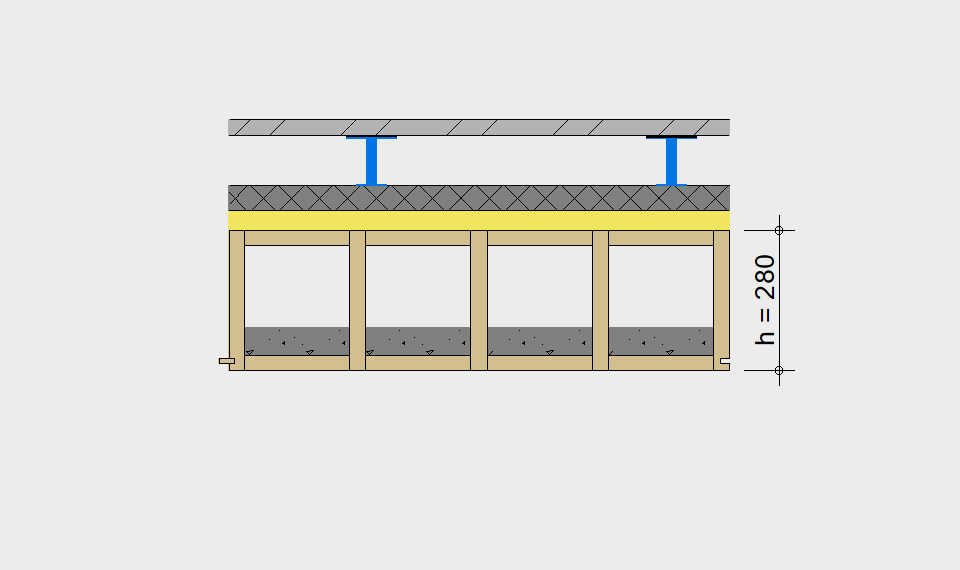
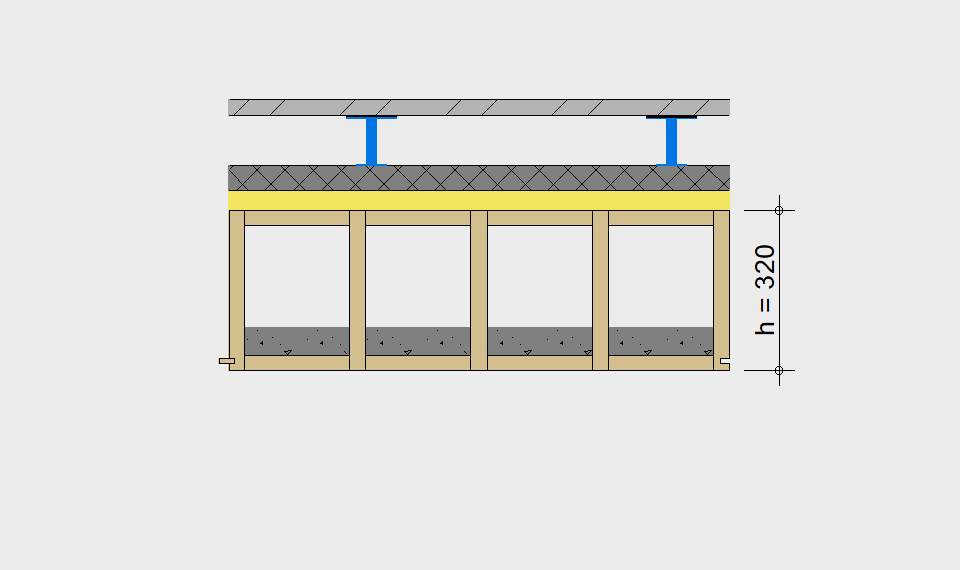
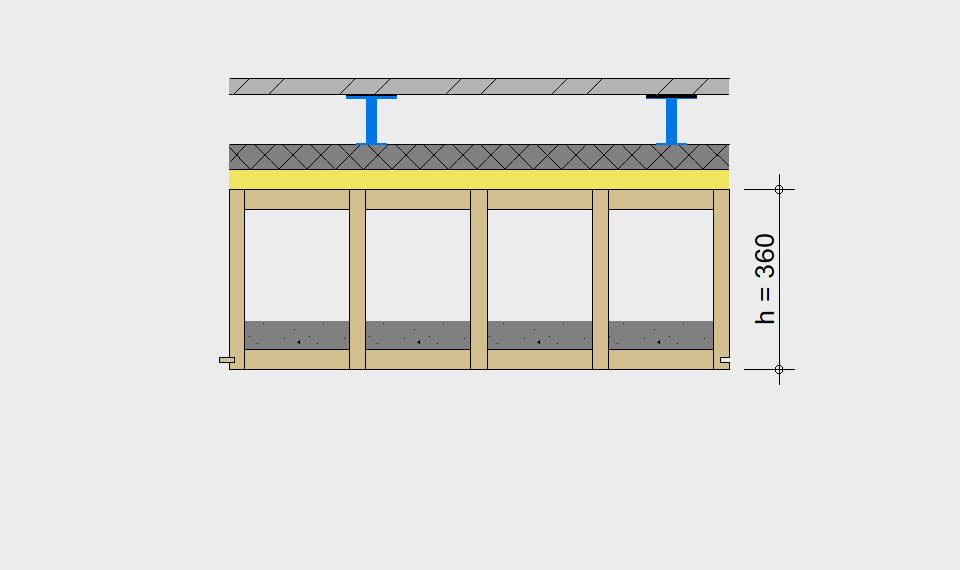
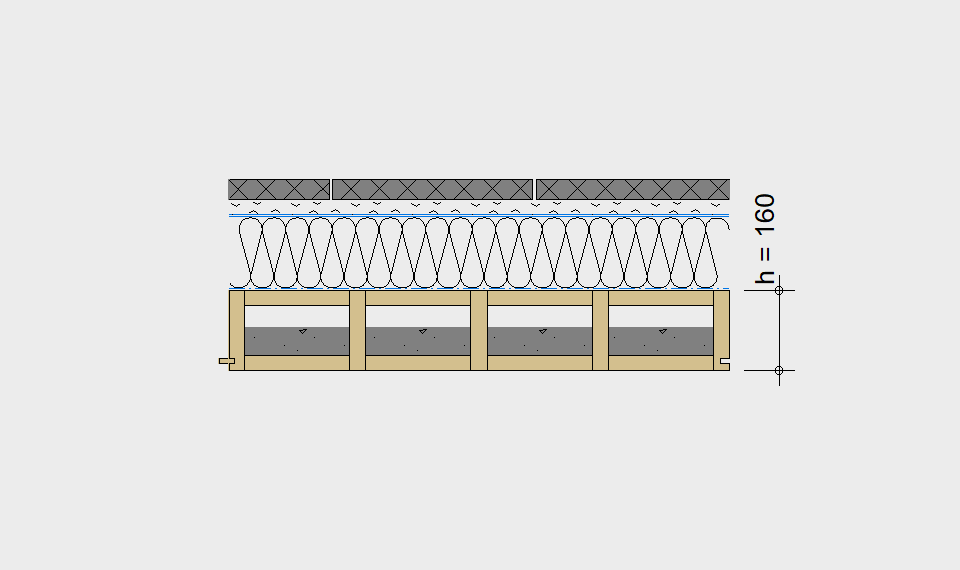
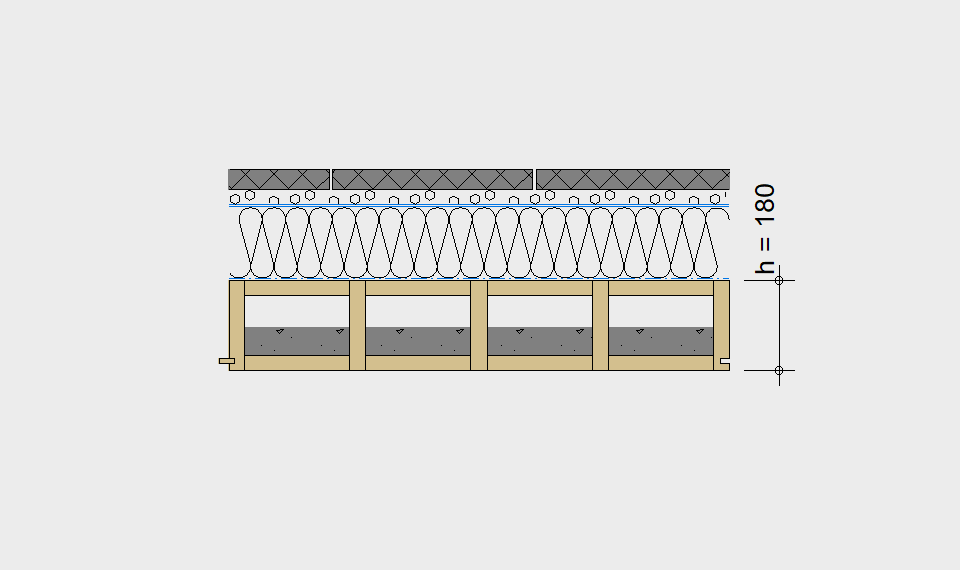
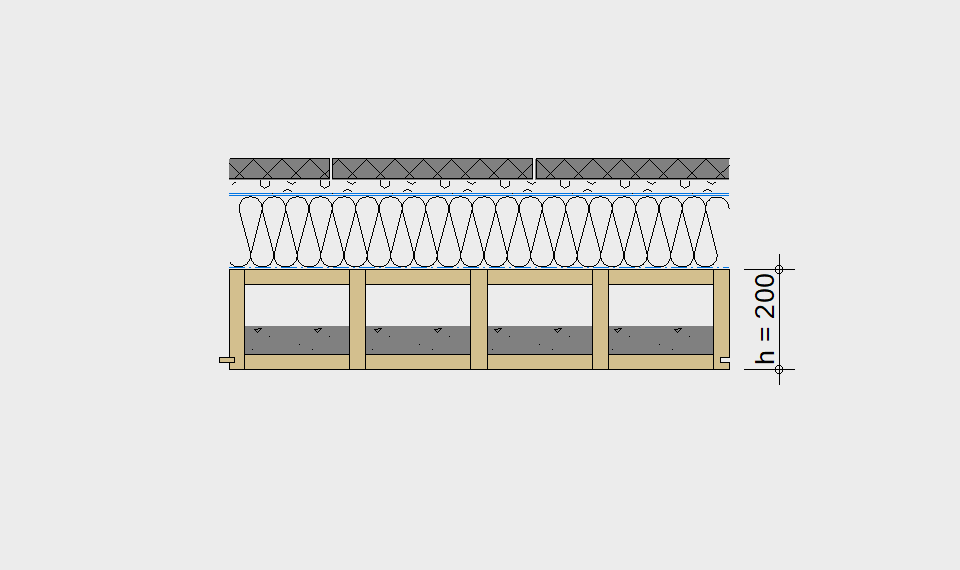
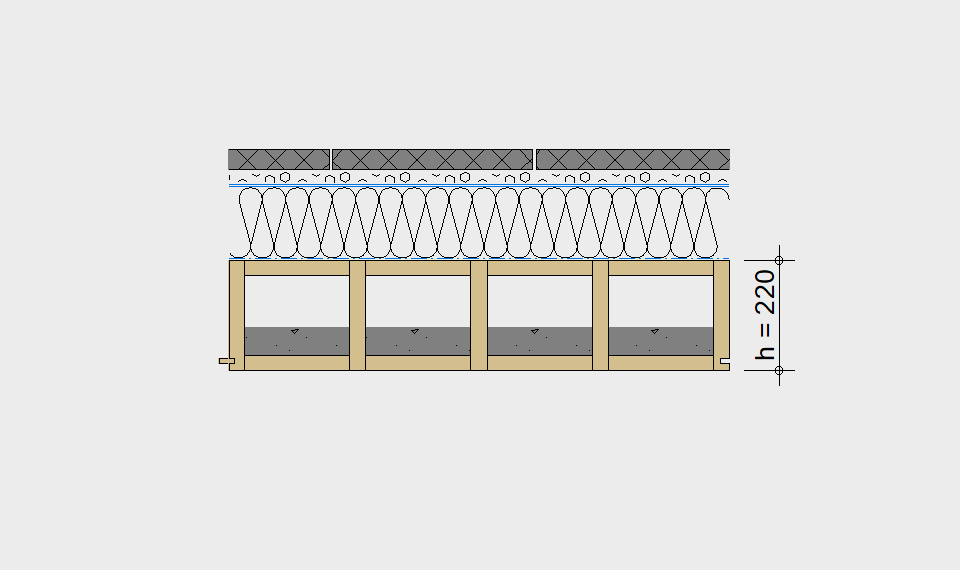
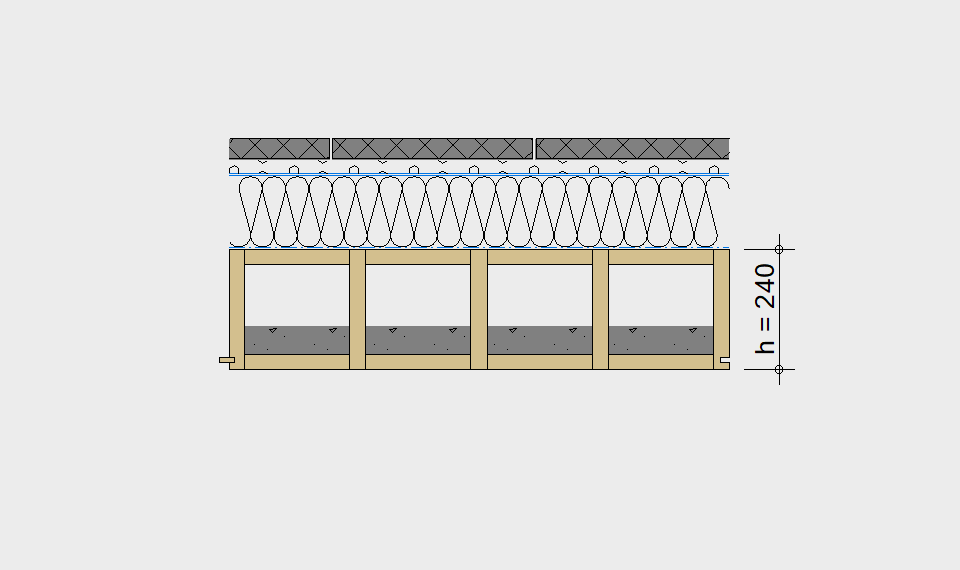
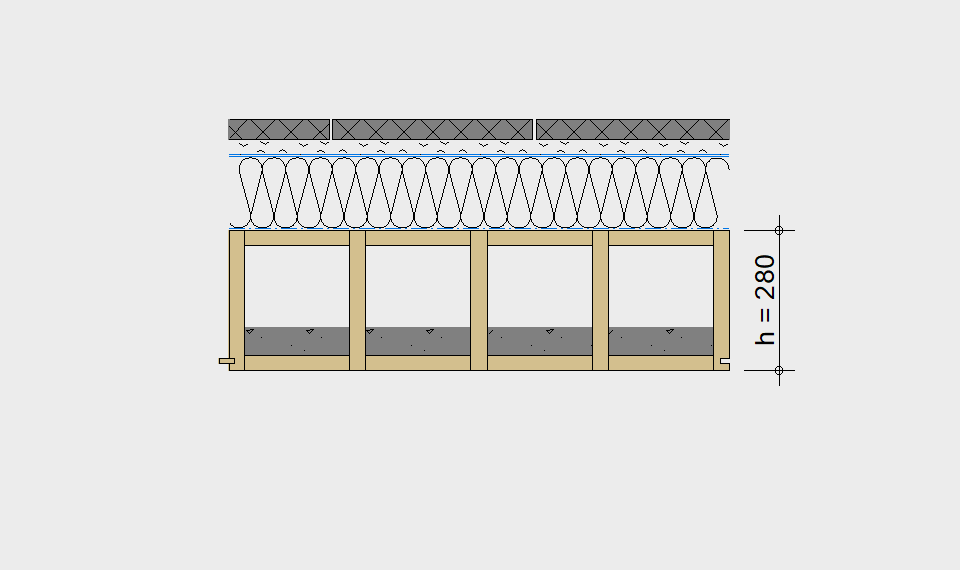
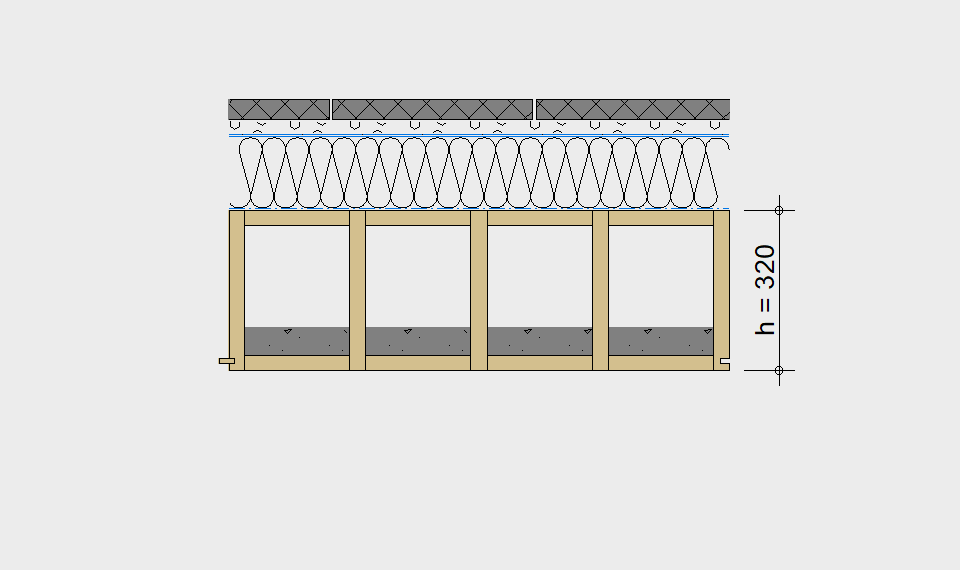
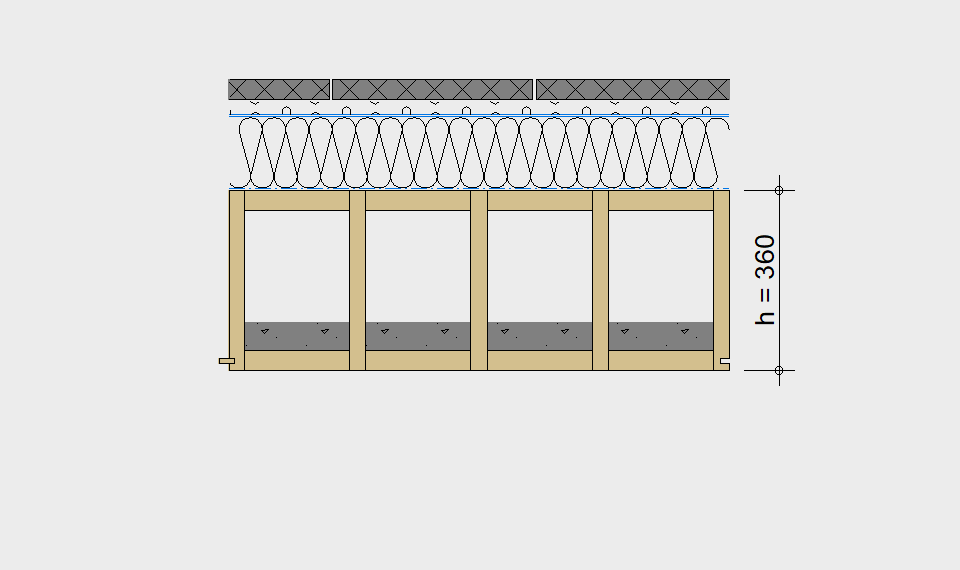
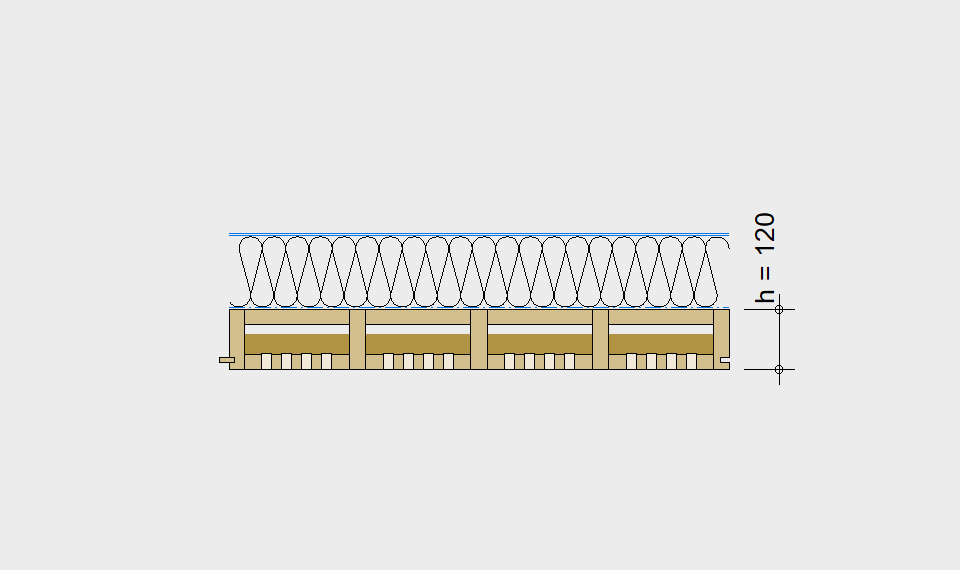
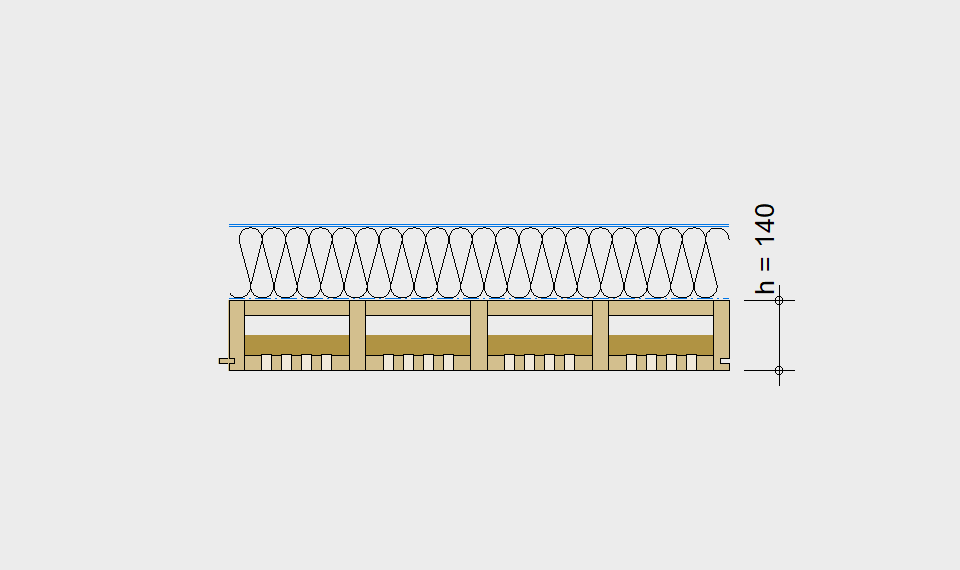
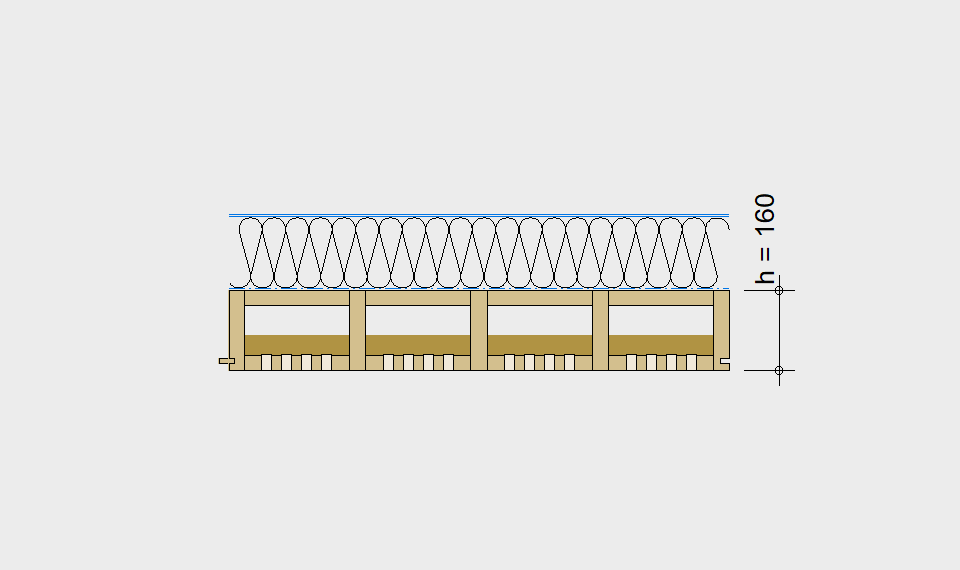
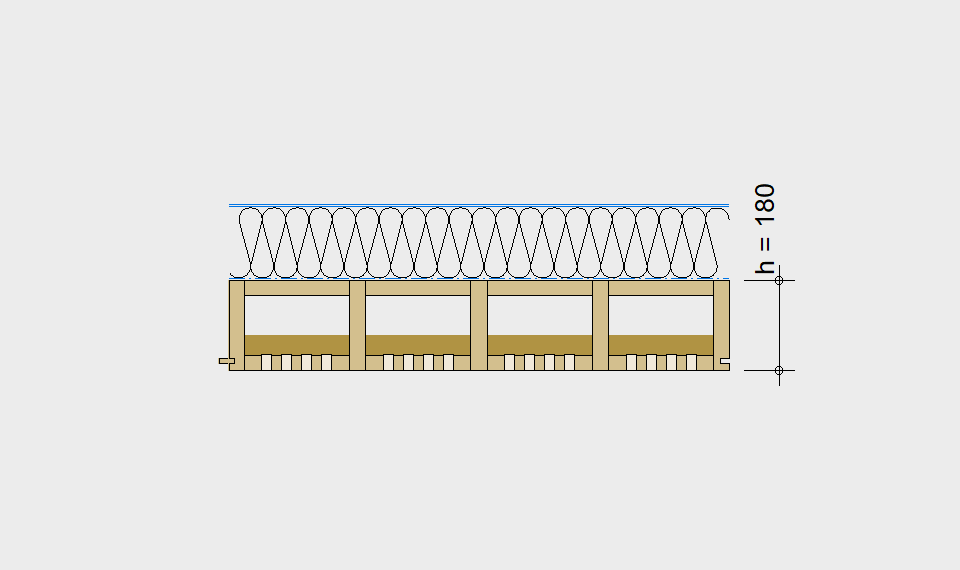
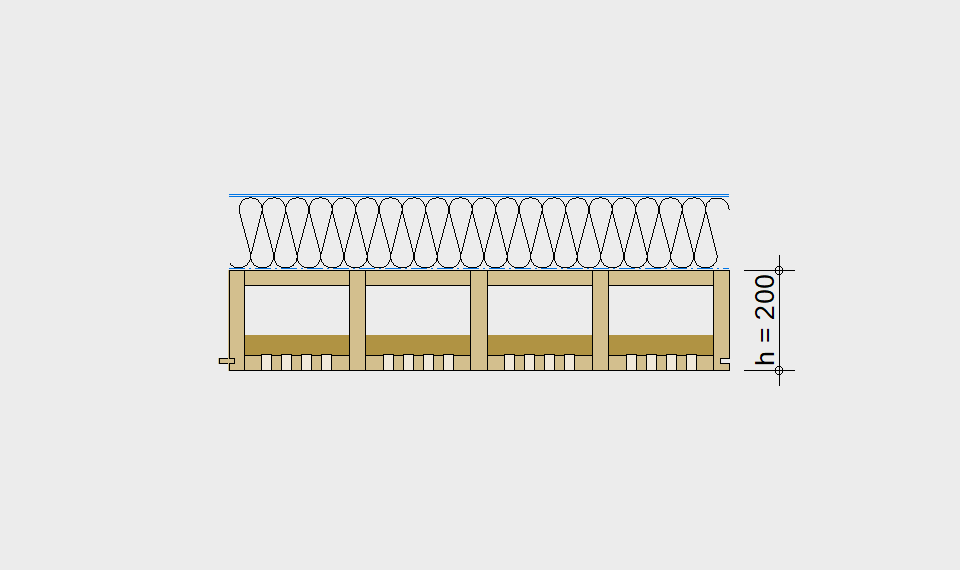
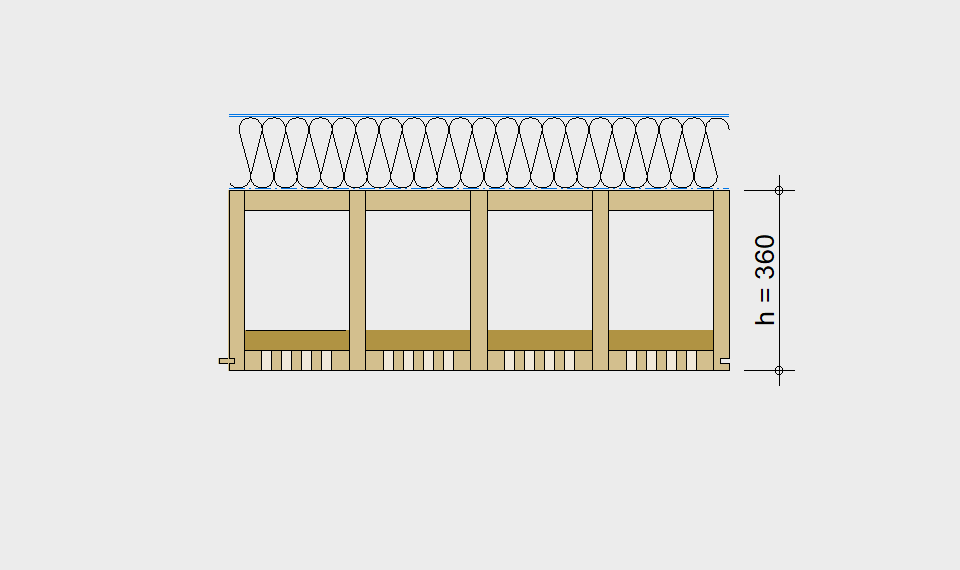
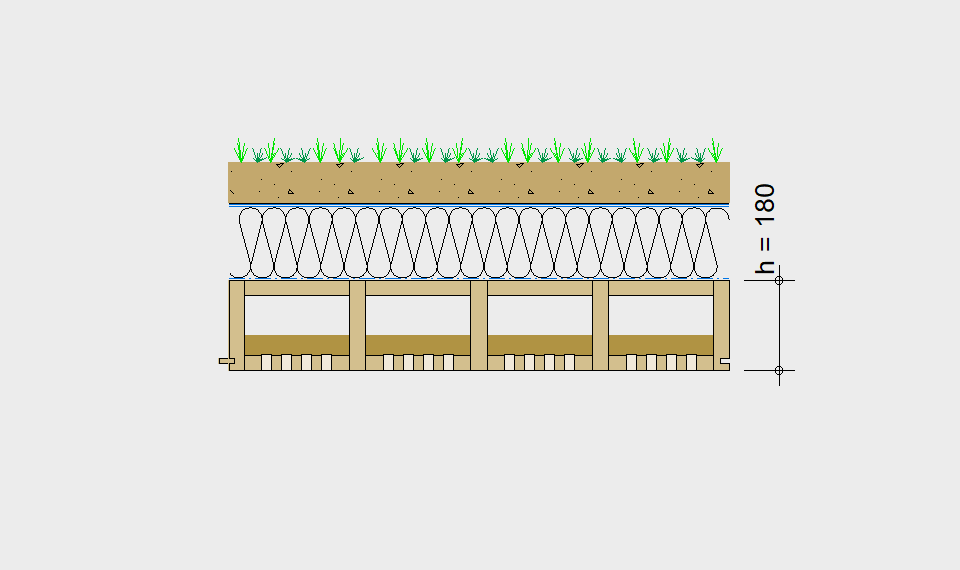
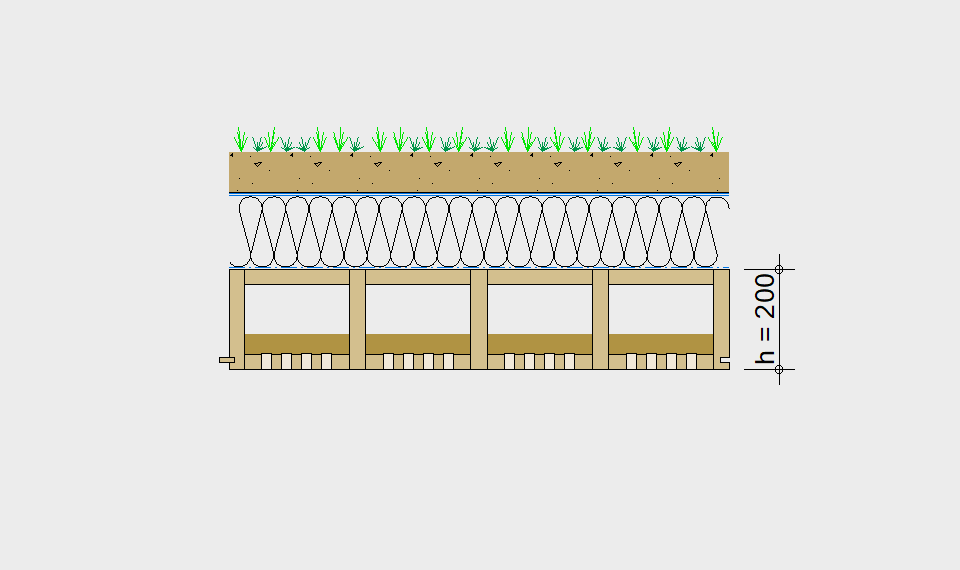
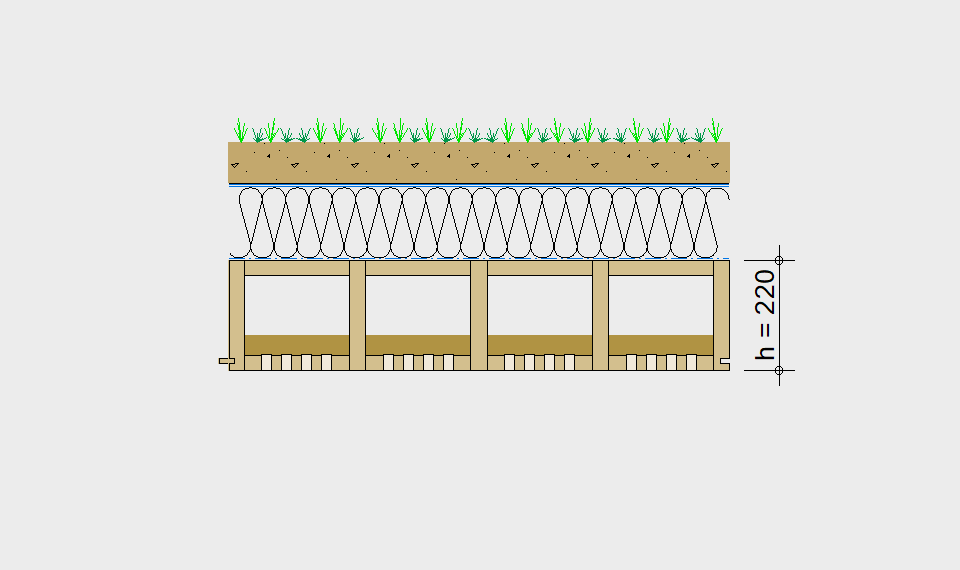
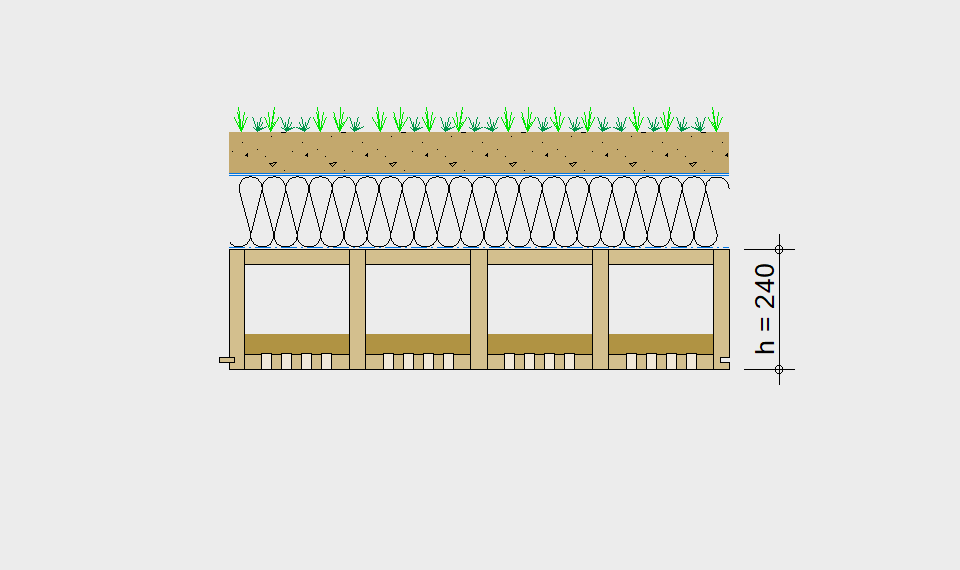
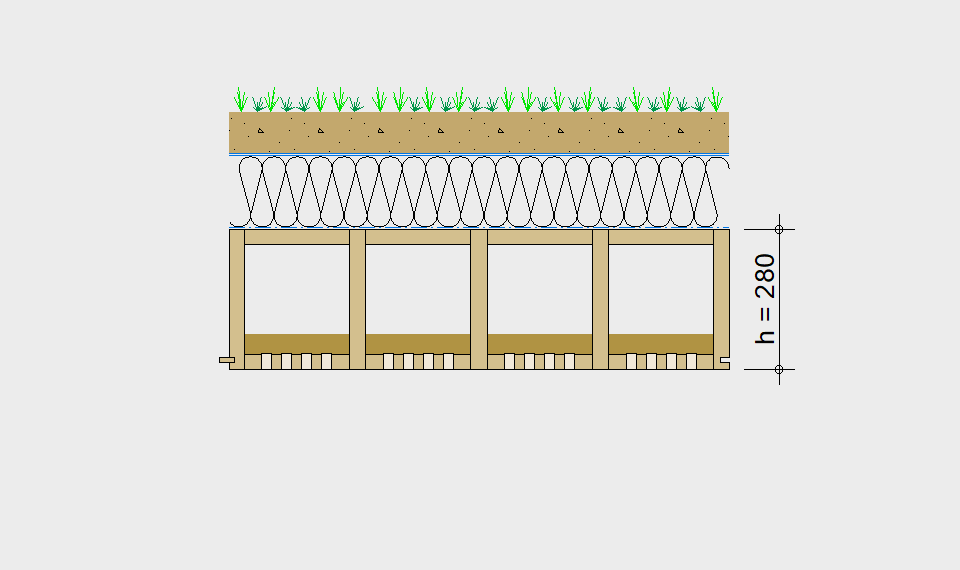
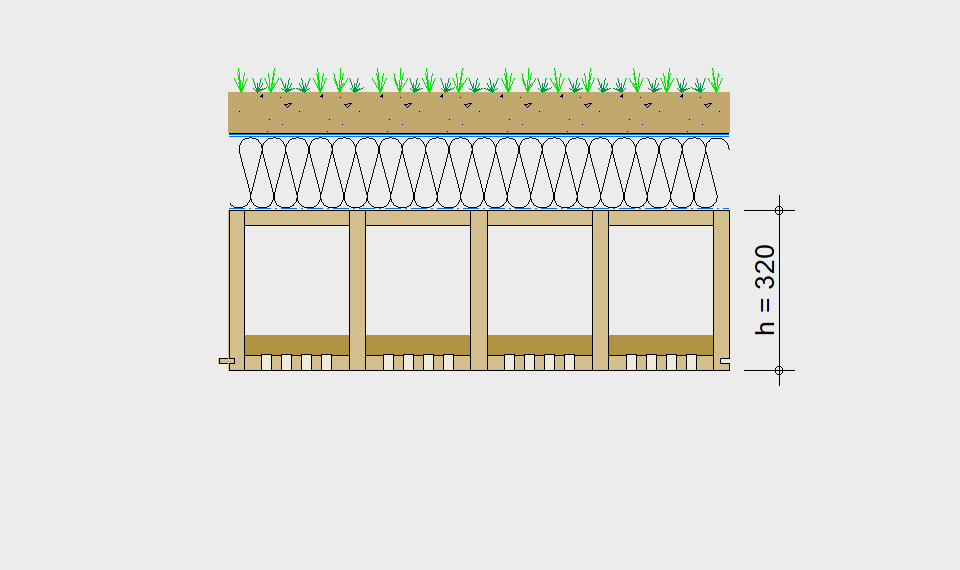
LIGNATUR elements feature very rigid load-bearing characteristics. The construction height required, based on the load, is comparable to that of a concrete floor.
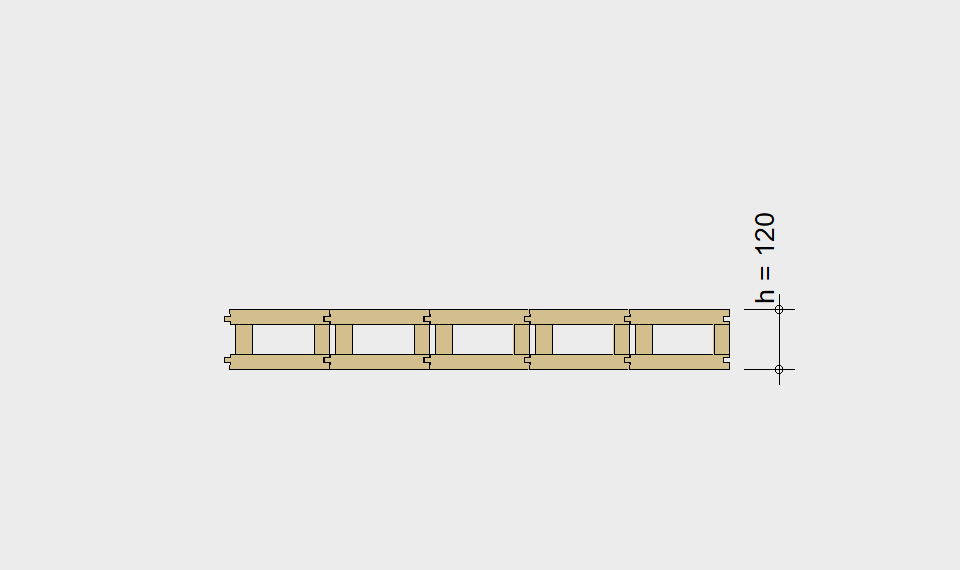
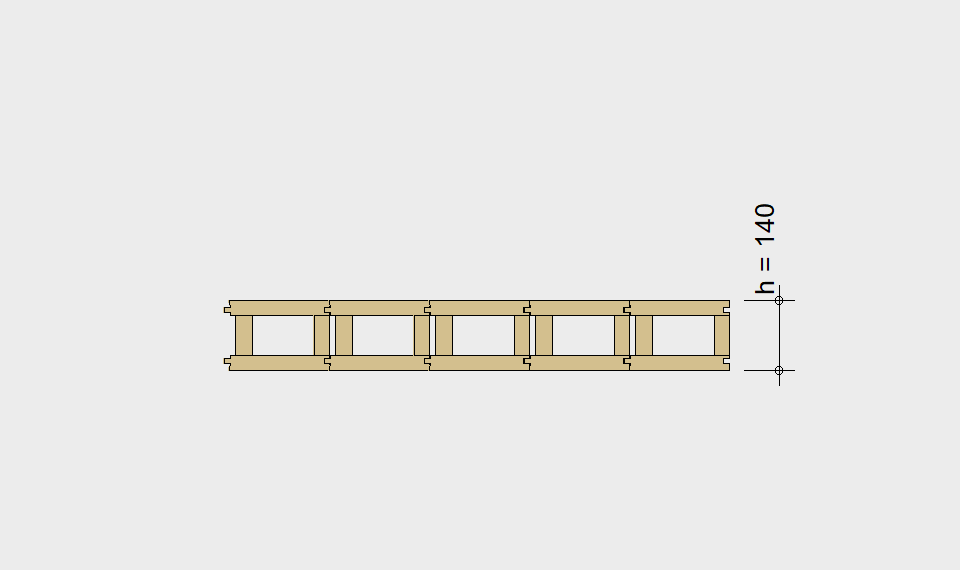
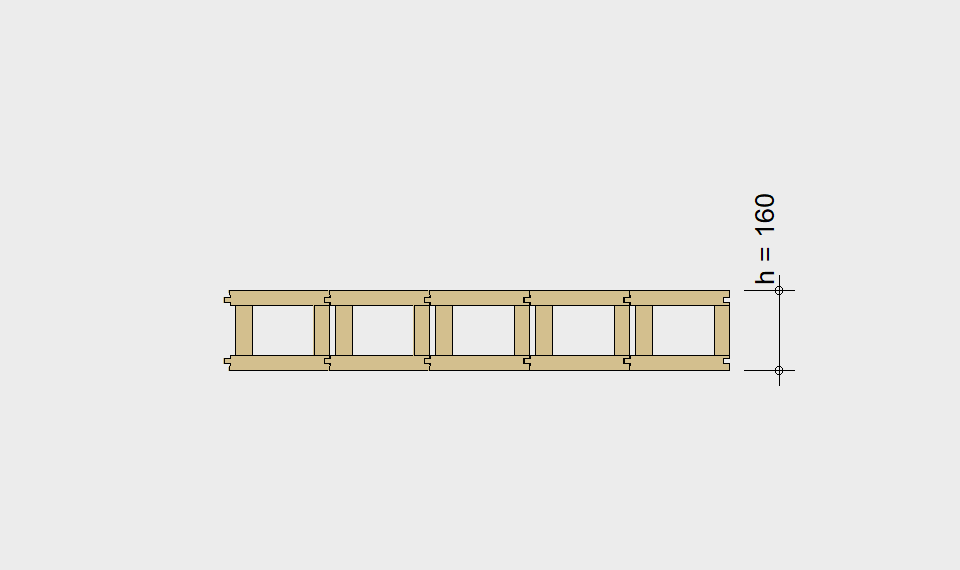
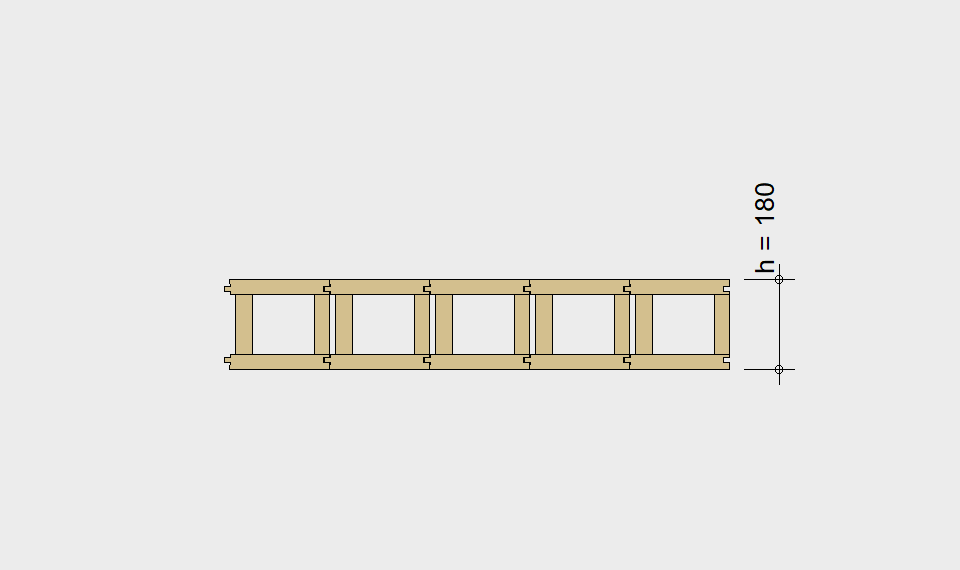
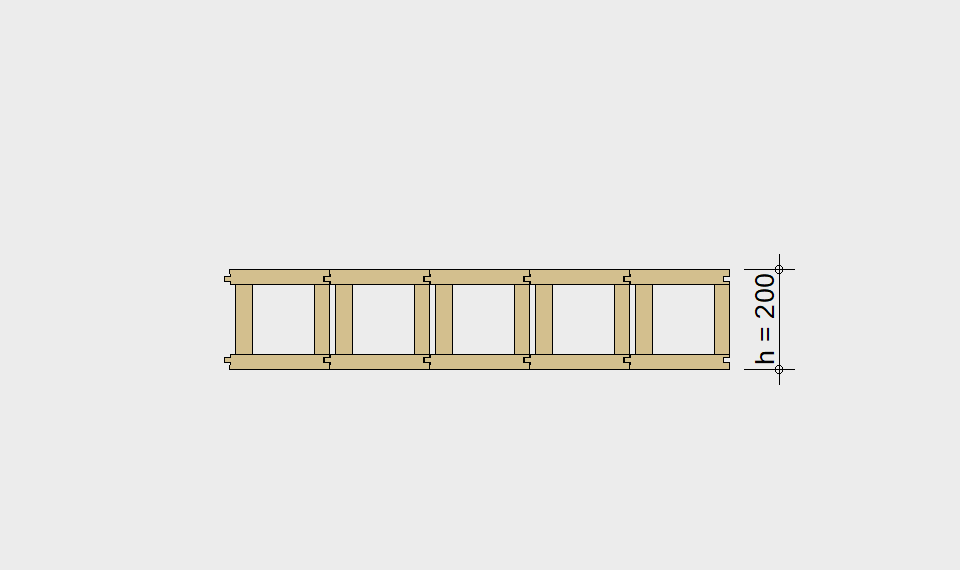
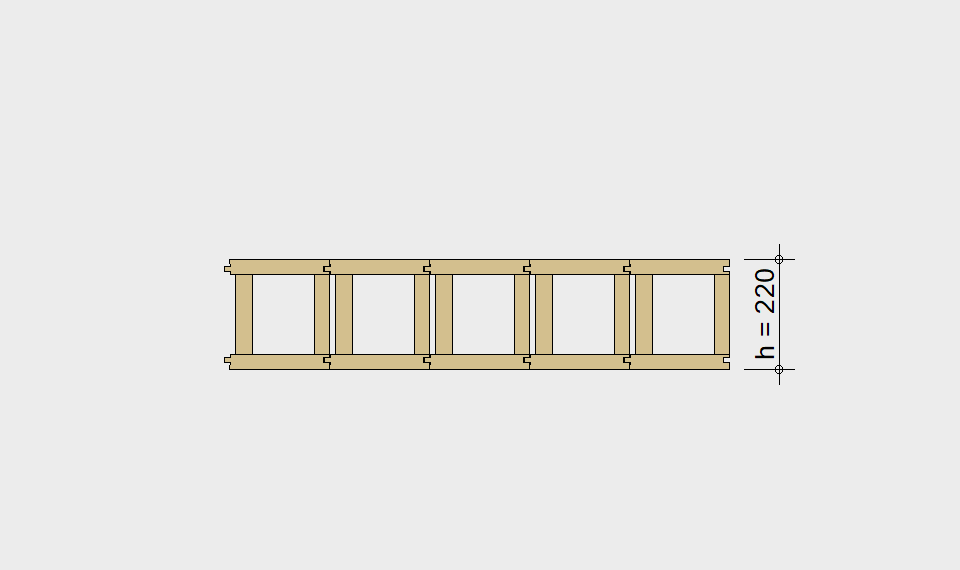
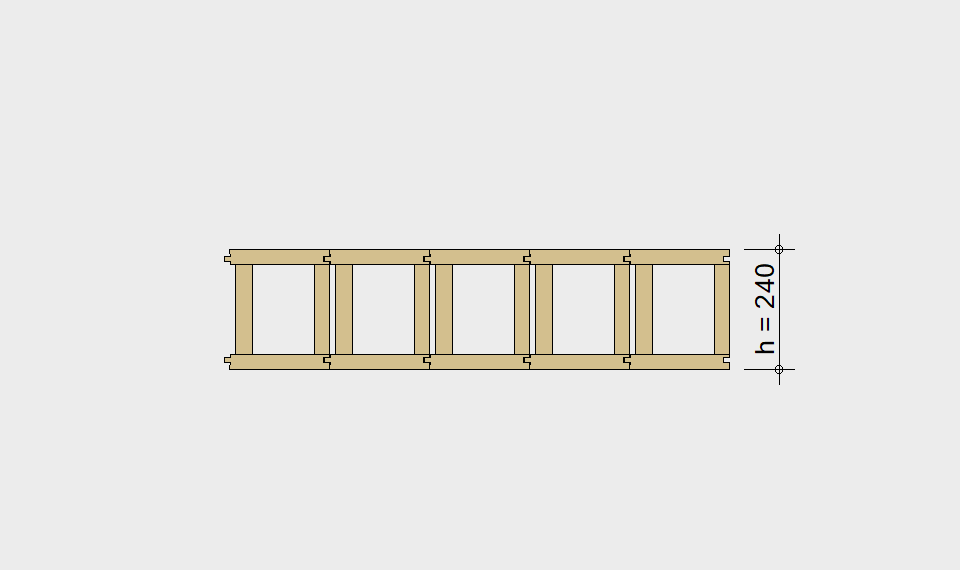
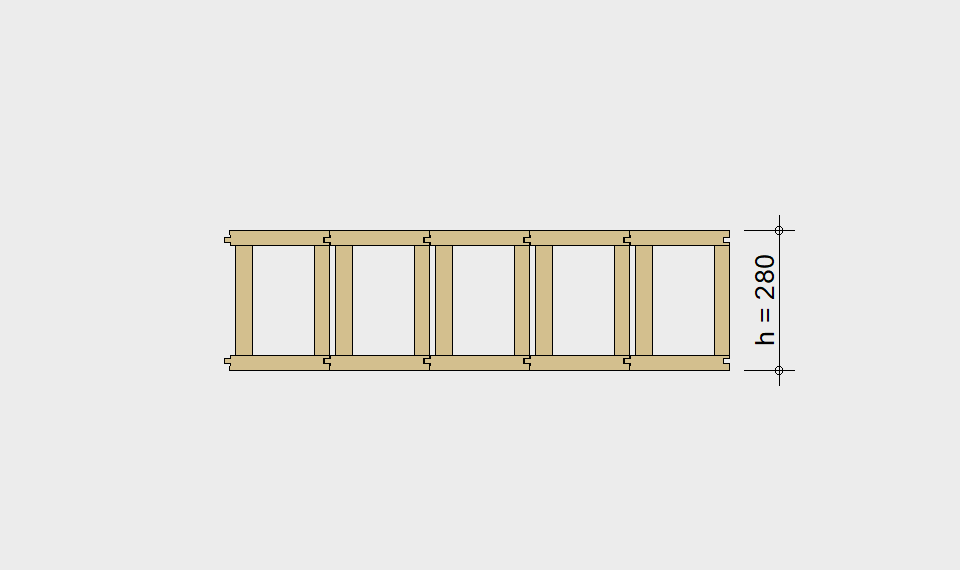
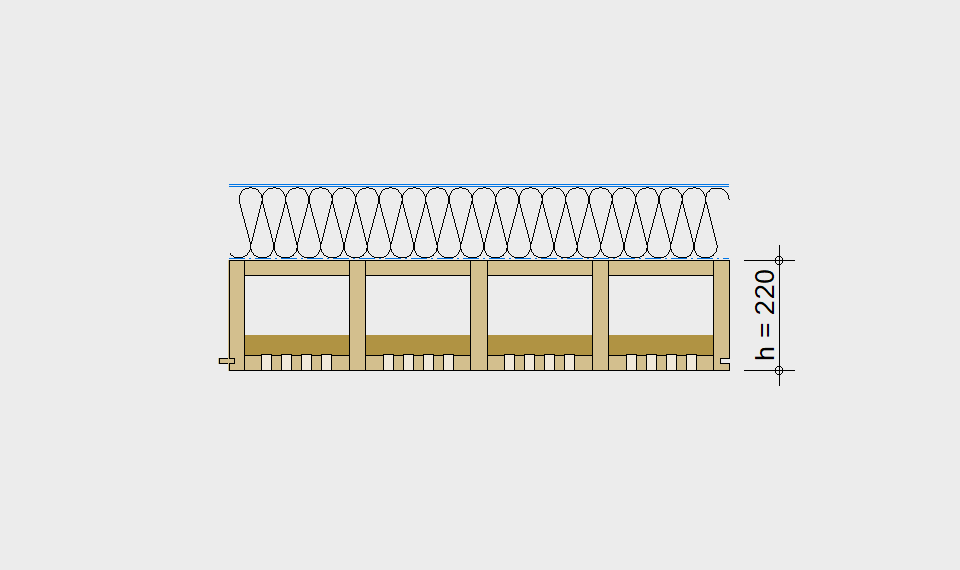
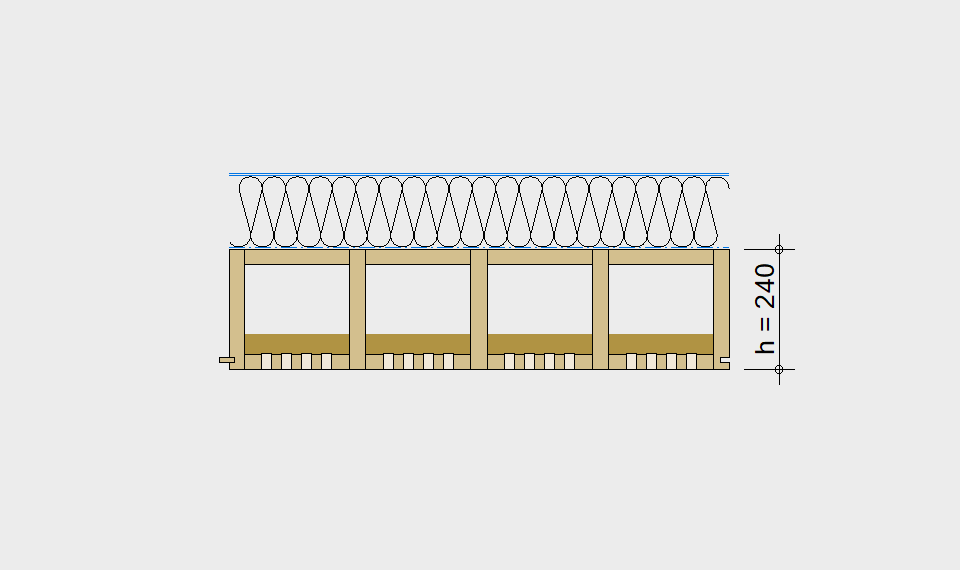
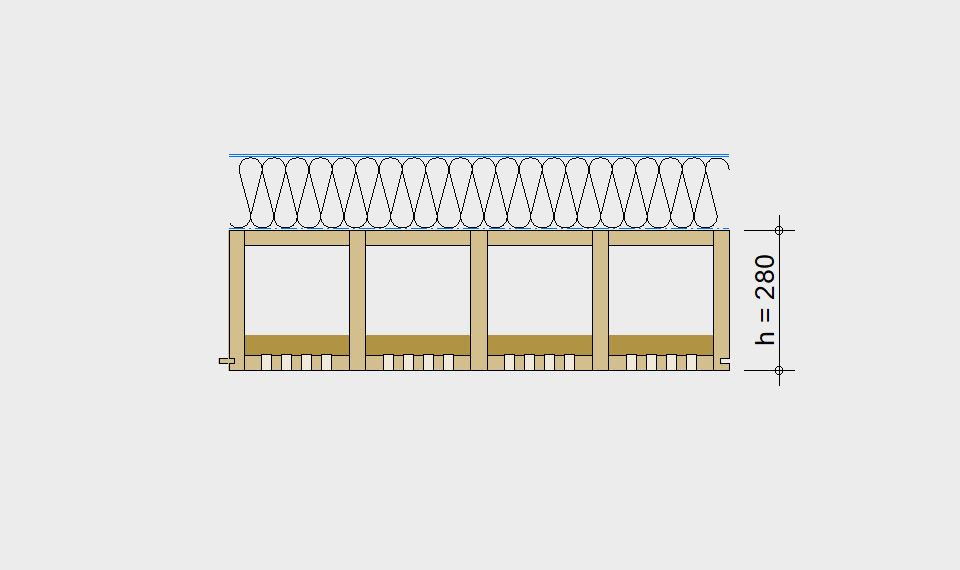
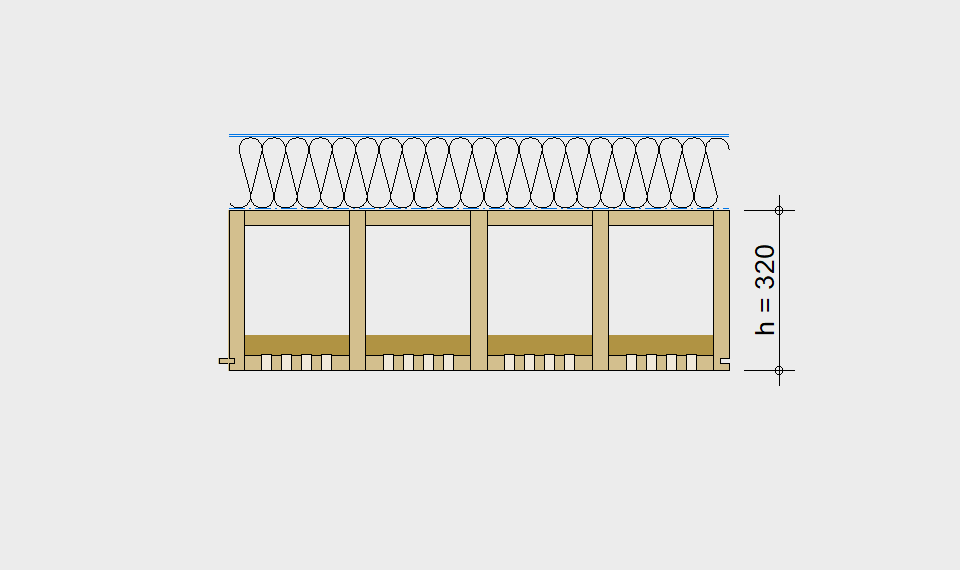
LIGNATUR box elements (LKE) are available from 120 to 320mm in height, surface elements (LFE) from 90 to 480mm in height. You can easily predimension your elements with the following diagrams and tables or contact our team. We are happy to assist with the dimensioning.

Floor design
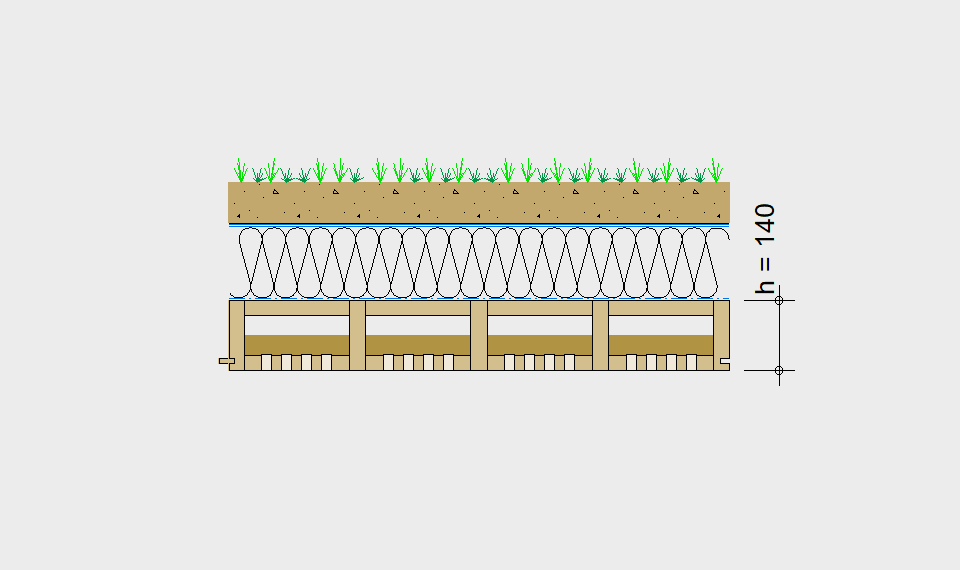
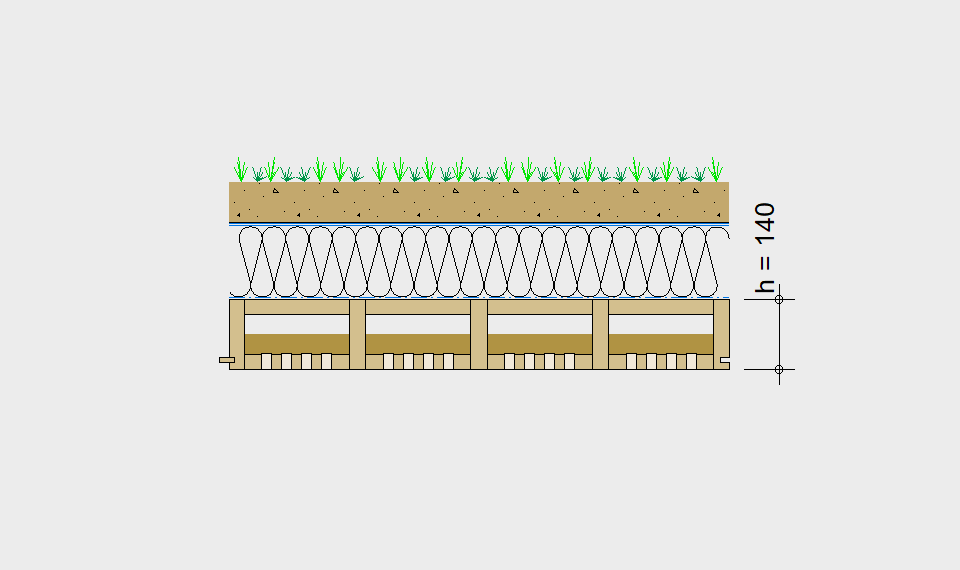
Are you designing the floor for a school, an office, a single or multi-family house, or an accessible roof?
For each application, the desired span can be selected in the drop-down menu. The required component dimensioning of LIGNATUR surface elements is displayed graphically. The floor structures shown are recommendations, tailored to the application.
Do you have any further questions? We'll be glad to advise you.

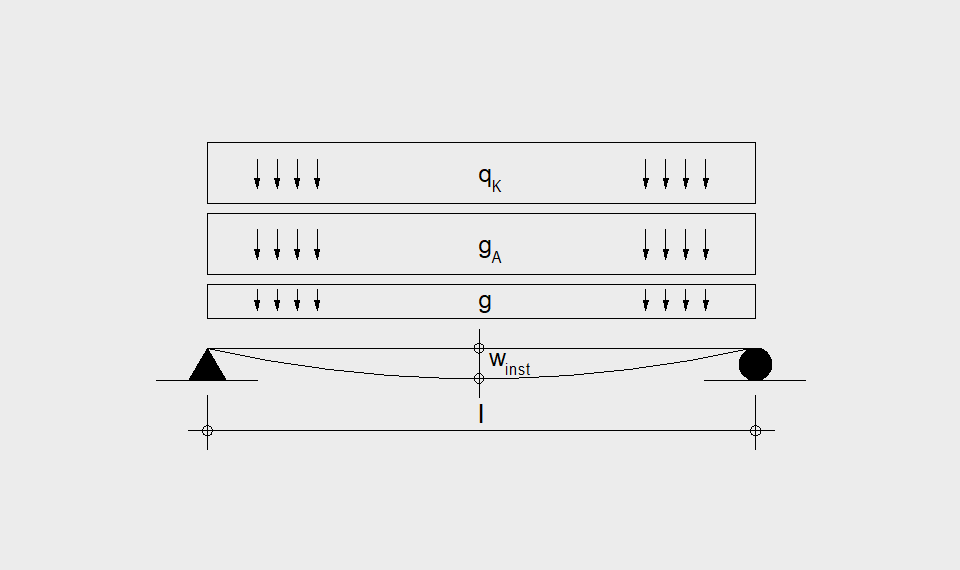
Static System – single-span beam
Ultimate limit state, serviceability limit state, and vibration design are fulfilled for all floor systems shown
- Dead load incl. fill g
- Load of floor construction gA
- Permanent load gk = g + gA
- Variable load qk
- Initial deflection winst (gK + qK)
Static roof
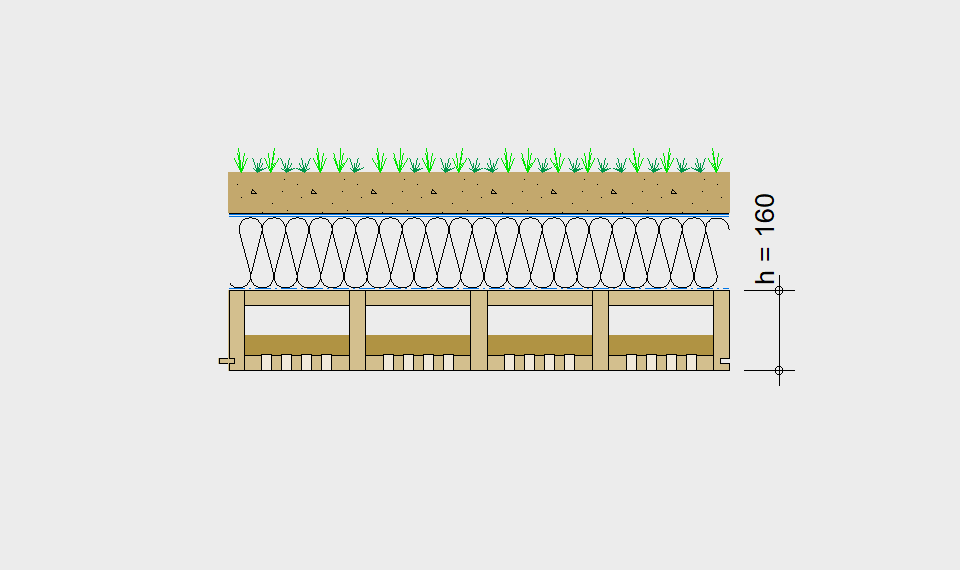
Are you planning a roof for a sports hall or an indoor swimming pool?
The desired span for the roof can be selected in the drop-down menu. The required component dimensioning of LIGNATUR surface elements is displayed graphically.
Do you have any further questions? We'll be glad to advise you.